MYOCARDITIS – Etiology, Pathophysiology, Signs and Symptoms, Diagnostic Evaluation and Management
Introduction
Any of the heart’s layers is affected by an infectious process. The infections are named for the layer of the heart most involved in the infectious process
DEFINTION OF MYOCARDITIS
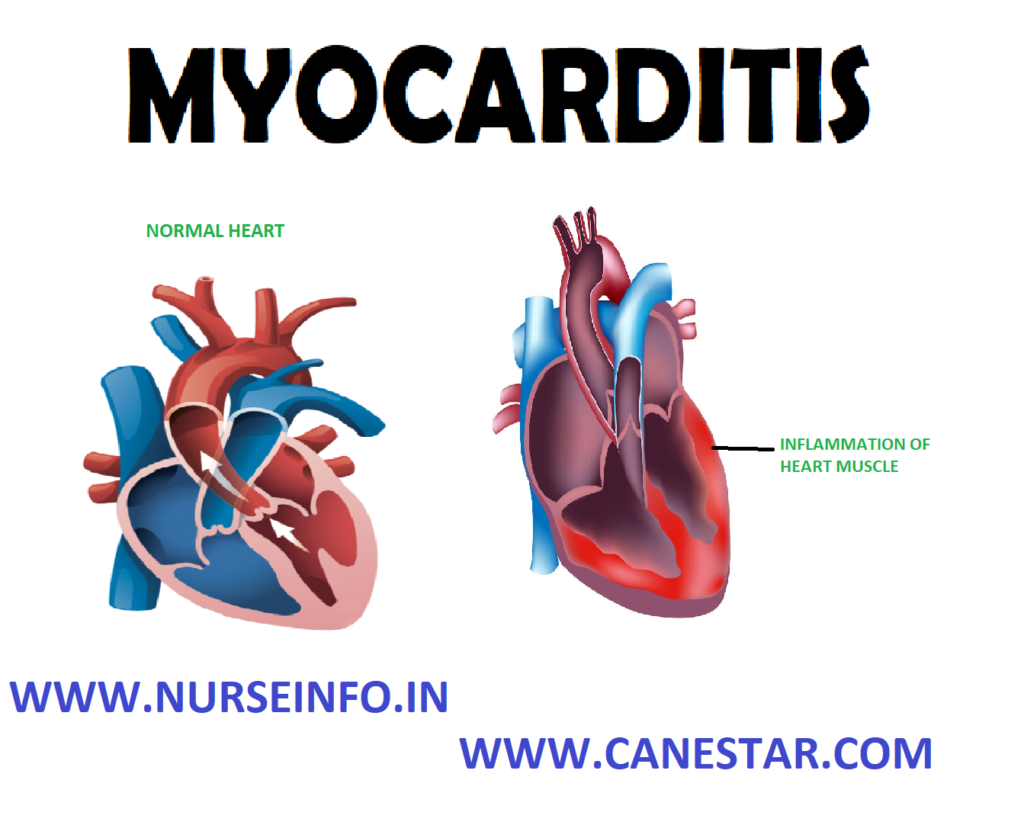
Myocarditis or inflammatory cardiomyopathy is the inflammation of heart muscles (myocardium)
Or
Myocarditis is the inflammation process involving the myocardium, can cause heart dilation, thrombi on the heart wall (mural thrombi), infiltration of circulating blood cells around the coronary vessels and between the muscle fibers, and degeneration of the muscle fibers themselves
ETIOLOGY
- Infections (viral(HIV, rubella, polio, cytomegalo, human herpes and hepatitis C), Protozoan (Toxoplasma gondii), bacterial (brucella, corynebacterium diphtheria), Fungal (aspergillus), Parasitic (ascaris, echinococcus granulosus)
- Toxins (drugs)
- Immunological causes: (allergic (acetazolamide, amitriptyline), rejection after a heart transplant, autoantigens (scleroderma, systemic lupus erythematosus), toxins (arsenic, toxic shock syndrome toxin, carbon monoxide, or snake venom), heavy metals (copper or iron)
- Physical agents: (electric shock, hyperpyrexia, radiation)
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Due to etiological agents – viruses, bacteria, protozoa etc —- inflammation around coronary vessels and between muscle fibers —- thrombus formation, heart dilatation, infiltration of blood cells —– degeneration of the muscle fibers
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
- Chest pain (often described as ‘stabbing’ in character)
- Palpitations
- Fever and other signs of infection, including headache, muscle aches, sore throat, diarrhea or rashes
- Fatigue
- Dyspnea
- Joints pain or swelling
- Leg swelling
- Dysrhythmias can also occur
- Fainting (often related to irregular heart rhythms)
- Low urine output
DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATIONS
Physical examination may reveal the following:
- Abnormal heartbeat or heart sounds (murmurs, extra heart sounds)
- Fever
- Fluid in lungs
- Rapid heartbeat (tachycardia)
- Swelling in the legs
- Chest X-ray: it shows enlarged cardiac silhouette resulting from ventricular enlargement or pericardial effusion
- Blood test: it shows moderate leukocytes (elevated cardiac enzymes, antibodies are found against the heart muscle and the body itself)
- ECG (it help to identify heart chamber size and ventricular functioning) it shows a bundle block or complete AV heart block, ST segment elevation or T-wave flattening
- Biopsy: it shows features of myocardial interstitium with abundant edema and inflammatory infiltrates, rich in lymphocytes and macrophages. Focal destruction of myocytes explains the myocardial pump failure
- Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI or CMR): It helps in diagnosing myocarditis by visualizing markers for inflammation of the myocardium
TREATMENT
- As most viral infections cannot be treated with directed therapy, symptomatic treatment is the only form of therapy for those forms of myocarditis
- In the acute phase, supportive therapy, including bed rest, is indicated
- For symptomatic patients, digoxin and diruretics provide clinical improvement
- For patients with moderate to severe dysfunction, cardiac function can be supported by use of inotropes such as Milrinone in the acute phase, followed by oral therapy with ACE inhibitors (captopril, lisinopril) when tolerated
- People who do not respond to conventional therapy are given bridge therapy with left ventricular assist devices. Heart transplantation is reserved
- For patients who fail to improve with conventional therapy, heart transplantation is reserved. Others: anti-embolism stockings and passive and active exercises should be used because embolization from various thrombosis and mural thrombi can occur, especially in patients on bed rest
COMPLICATIONS
- Cardiomyopathy
- Pulmonary congestion
- Pericarditis
- Heart failure
- Sudden death
PREVENTION
Prevention of infectious diseases by means of appropriate immunizations (e.g. influenza, hepatitis) and early treatment appear to be important in decreasing the incidence of myocarditis