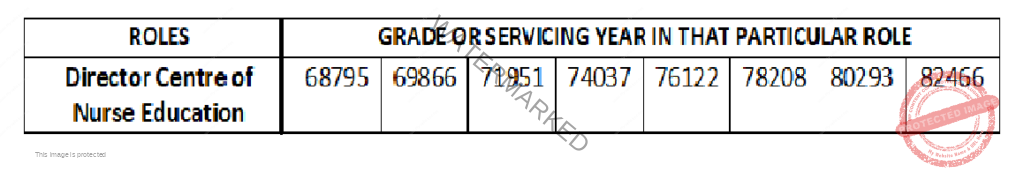
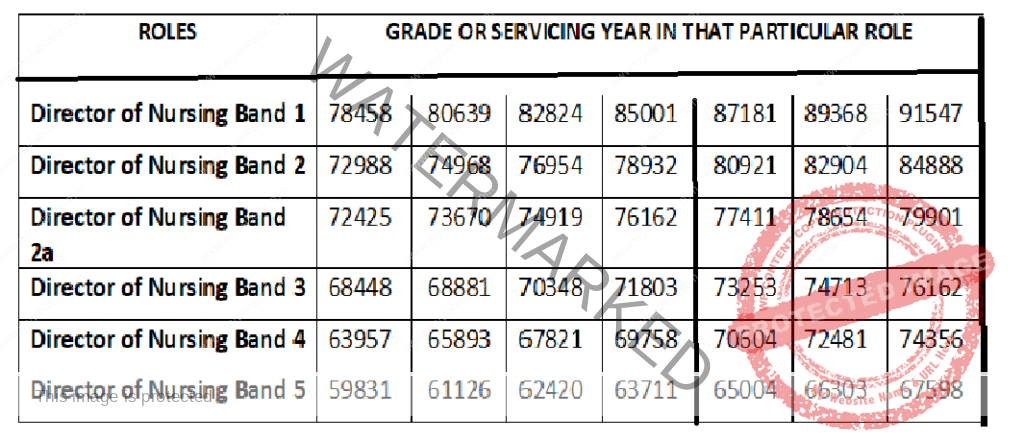
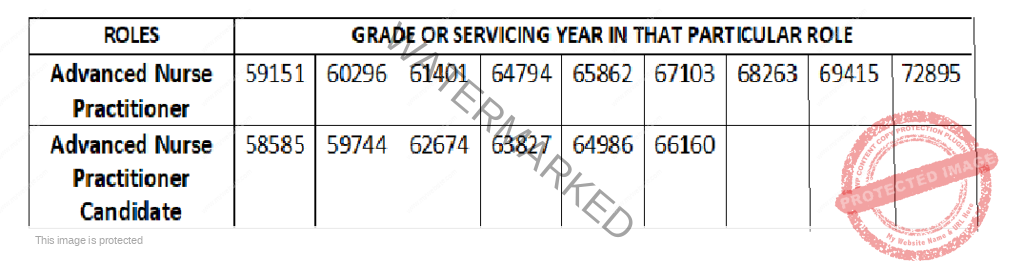
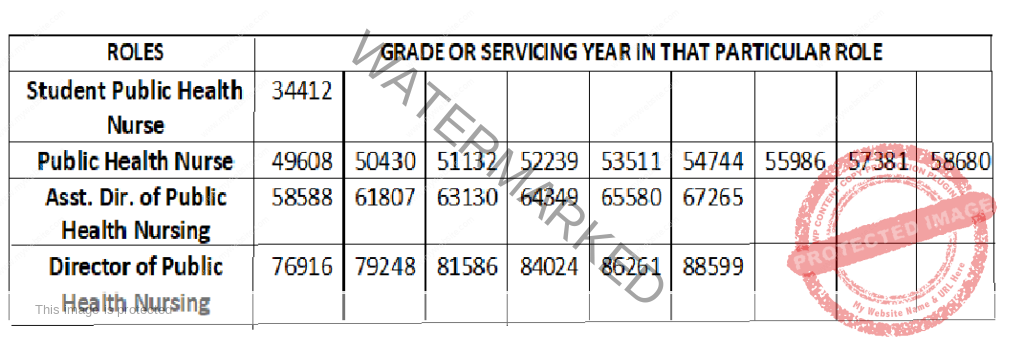
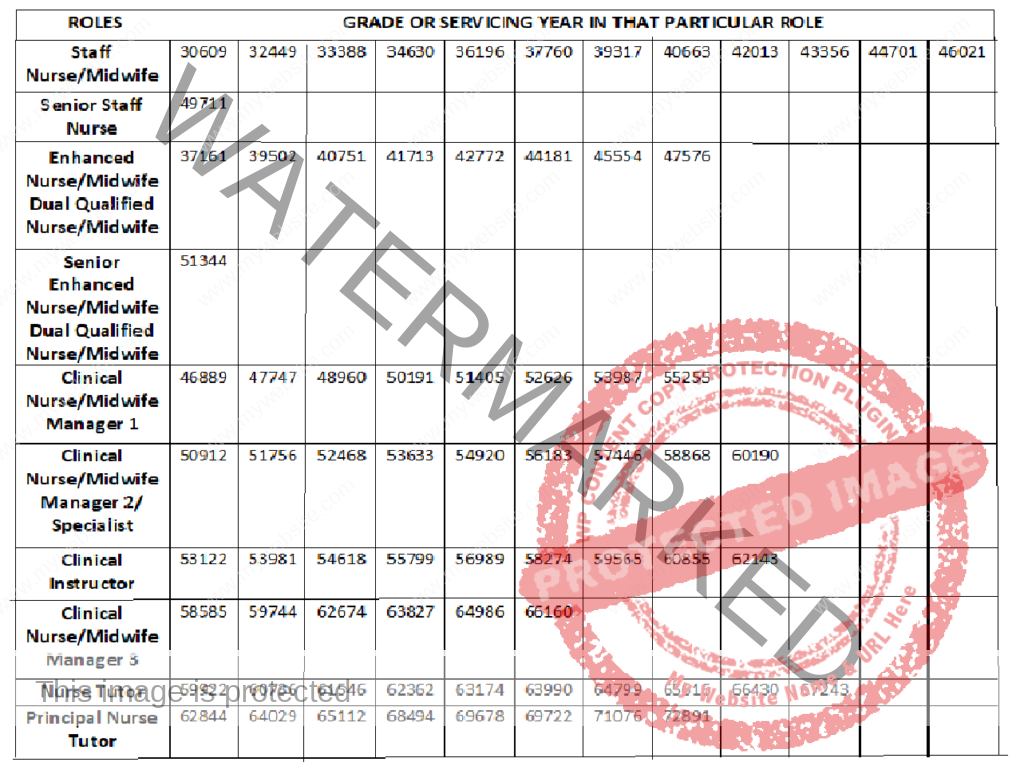
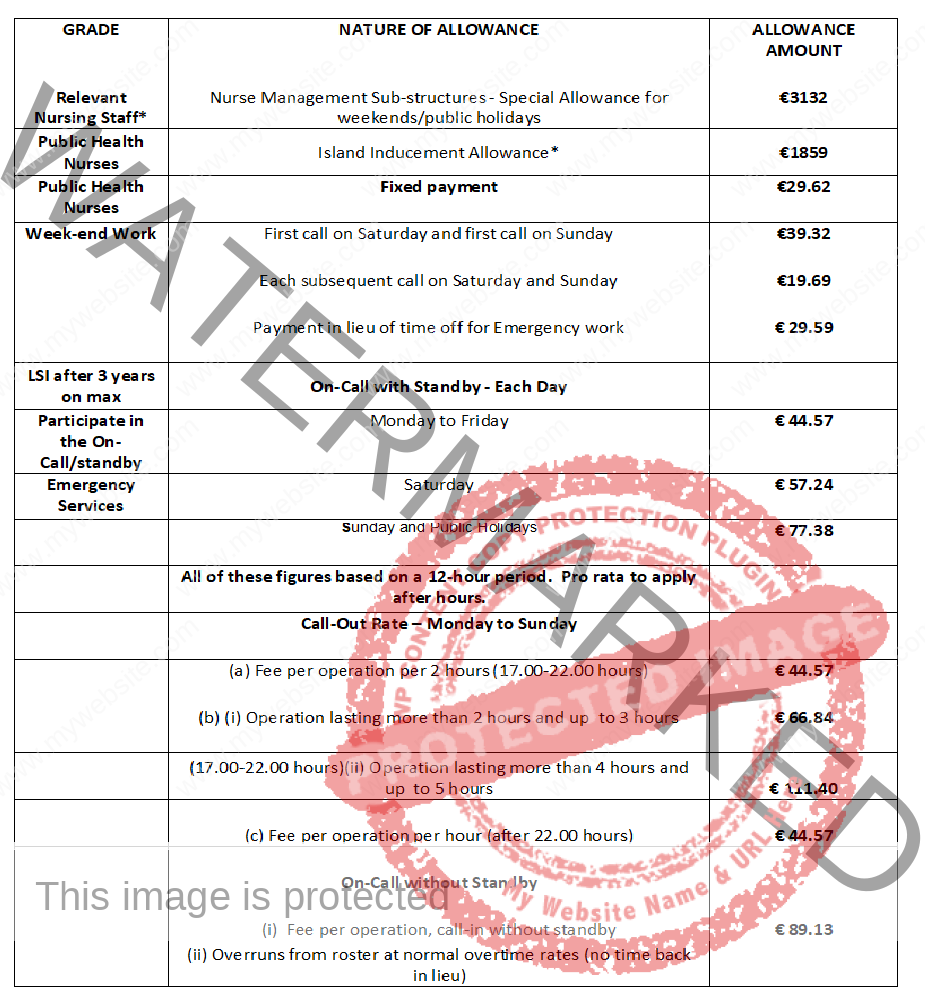
NURSES SALARY IN BAHRAIN, IRAQ AND OMAN
The factors that define the nurse salary are location, experience and education. Job title also plays a vital role in determining the nurse salary.
BAHRAIN
Bahrain offers good nursing salary about 14,300 BHD per annum. Average salary of nurses is 1,190 BHD per month, the lowest salary is 560 BHD per month and highest salary for nurses is 1,880 per month
Staff nurse salary 14300 BHD per Annum.
Average salary – 1,190 BHD per month, lowest salary – 560 BHD per month and highest salary – 1,880 per month (for more salary details scroll down)
Staff Nurse Salary by Experience
Staff nurse earn good if they have good experience, for instance, the nurse with 20 + year experience earns 1,780 per month. Nurses with less than 2 years of experience or fresher earn 650 BHD per month. Depending on experience, the nurse’s salary will be increased each year.
Less than 2 years – 650 BHD per month
2 to 5 years – 890 BHD per month
5 to 10 years – 1,270 BHD per month
10 to 15 years – 1,550 BHD per month
15 to 20 years – 1,630 BHD per month
20 + years – 1,780 BHD per month
Salary Based on Education
Degree plays a vital role in determining the salary for nurses. For example, nurse with bachelor degree get 890 BHD per month and nurse with master degree, will get 1,630 BHD per month
Nurse with Bachelor Degree – 890 BHD per month
Nurse with Master Degree – 1,630 BHD per month
Nurse Salary with Different Job Title
Based on job title the nurse’s salary will be greatly varied. With experience and job title, the nurse’s salary will be good, for example, nursing director earn about 2960 BHD per month, “Nurse” title earn 1380 BHD per month.
| JOB TITLE | SALARY (BHD per month) |
| Acute Care Nurse | 1340 |
| Assistant Director of Nursing | 2130 |
| Case Manager | 1780 |
| Company Nurse | 1020 |
| Critical Care Nurse | 1370 |
| District Nurse | 1180 |
| Head Nurse | 1420 |
| Home Nurse | 1160 |
| ICU Registered Nurse | 1320 |
| Informatics Nurse Specialist | 1370 |
| Licensed Practical Nurse (LPN) | 1230 |
| MDS Coordinator | 1280 |
| Mental Health Nurse | 1310 |
| Neonatal Nurse Practitioner | 1660 |
| Nurse | 1380 |
| Nurse Midwife | 1380 |
| Nurse Practitioner | 1460 |
| Nursing Assistant | 1090 |
| Nursing Coordinator | 1440 |
| Nursing Director | 2960 |
| Nursing Services Instructor | 1310 |
| Nursing Supervisor | 1770 |
| Occupational Health Advisor | 2230 |
| Occupational Therapist | 1870 |
| Personal Support Worker | 970 |
| Psychiatric Nurse | 1190 |
| Registered Nurse | 1250 |
| Respiratory Manager | 2370 |
| School Nurse | 1080 |
| Staff Nurse | 1190 |
| Theatre Manager | 2040 |
| Utilization Review Nurse | 1240 |
IRAQ
In Iraq, the average staff nurse earns 1,980,000 IQD per month; lowest salary per month is 1,270,000 IQD per month highest salary for nurses is 3,810,000 IQD per month.
Average staff nurse salary – 1,980,000 IQD per month
Salary – 1,270,000 IQD (lowest) per Month and 3,810,000 IQD (highest) per Month
Nurse Salary with Job Title
Like other countries, Iraq provides good salary for nurses based on their job title and education. For example, respiratory manager earns good salary of about 3,400,000 IQD per month and head nurse earns 2060000 IQD per month
| JOB TITLE | SALARY (IQD per month) |
| Acute Care Nurse | 2010000 |
| Assistant Director of Nursing | 3140000 |
| Case Manager | 2290000 |
| Company Nurse | 1340000 |
| Critical Care Nurse | 1930000 |
| District Nurse | 1770000 |
| Head Nurse | 2060000 |
| Home Nurse | 1660000 |
| ICU Registered Nurse | 1750000 |
| Informatics Nurse Specialist | 1790000 |
| Licensed Practical Nurse (LPN) | 1670000 |
| MDS Coordinator | 1900000 |
| Mental Health Nurse | 1850000 |
| Neonatal Nurse Practitioner | 2330000 |
| Nurse | 1740000 |
| Nurse Midwife | 2100000 |
| Nurse Practitioner | 1980000 |
| Nursing Assistant | 1450000 |
| Nursing Coordinator | 1900000 |
| Nursing Director | 3840000 |
| Nursing Services Instructor | 1850000 |
| Nursing Supervisor | 2470000 |
| Occupational Health Advisor | 3130000 |
| Occupational Therapist | 2800000 |
| Personal Support Worker | 1310000 |
| Psychiatric Nurse | 1660000 |
| Registered Nurse | 1680000 |
| Respiratory Manager | 3460000 |
| School Nurse | 1490000 |
| Staff Nurse | 1620000 |
OMAN
In Oman, the nurse average salary is about 1,710 OMR per month; lowest is 1,100 OMR per month and highest salary for nurses is 3,290 OMR per month.
Nurse salary average – 1,710 OMR per month, lowest salary – 1,100 OMR per month and highest salary – 3,290 OMR
Nurse Salary by Job Title
In Oman, acute care nurse earn 1510 OMR per month, head nurse earn 1540 OMR per month and nursing director with good experience will get 3120 OMR per month.
| JOB TITLE | SALARY (OMR per month) |
| Acute Care Nurse | 1510 |
| Assistant Director of Nursing | 2450 |
| Case Manager | 1860 |
| Company Nurse | 1090 |
| Critical Care Nurse | 1600 |
| District Nurse | 1380 |
| Head Nurse | 1540 |
| Home Nurse | 1320 |
| ICU Registered Nurse | 1480 |
| Informatics Nurse Specialist | 1540 |
| Licensed Practical Nurse (LPN) | 1300 |
| MDS Coordinator | 1450 |
| Mental Health Nurse | 1420 |
| Neonatal Nurse Practitioner | 2010 |
| Nurse | 1410 |
| Nurse Midwife | 1640 |
| Nurse Practitioner | 1640 |
| Nursing Assistant | 1280 |
| Nursing Coordinator | 1610 |
| Nursing Director | 3120 |
| Nursing Services Instructor | 1600 |
| Nursing Supervisor | 2050 |
| Occupational Health Advisor | 2490 |
| Occupational Therapist | 2280 |
| Personal Support Worker | 1060 |
| Psychiatric Nurse | 1370 |
| Registered Nurse | 1370 |
| Respiratory Manager | 2750 |
| School Nurse | 1370 |
| Staff Nurse | 1370 |
| Theatre Manager | 2340 |
| Utilization Review Nurse | 1410 |