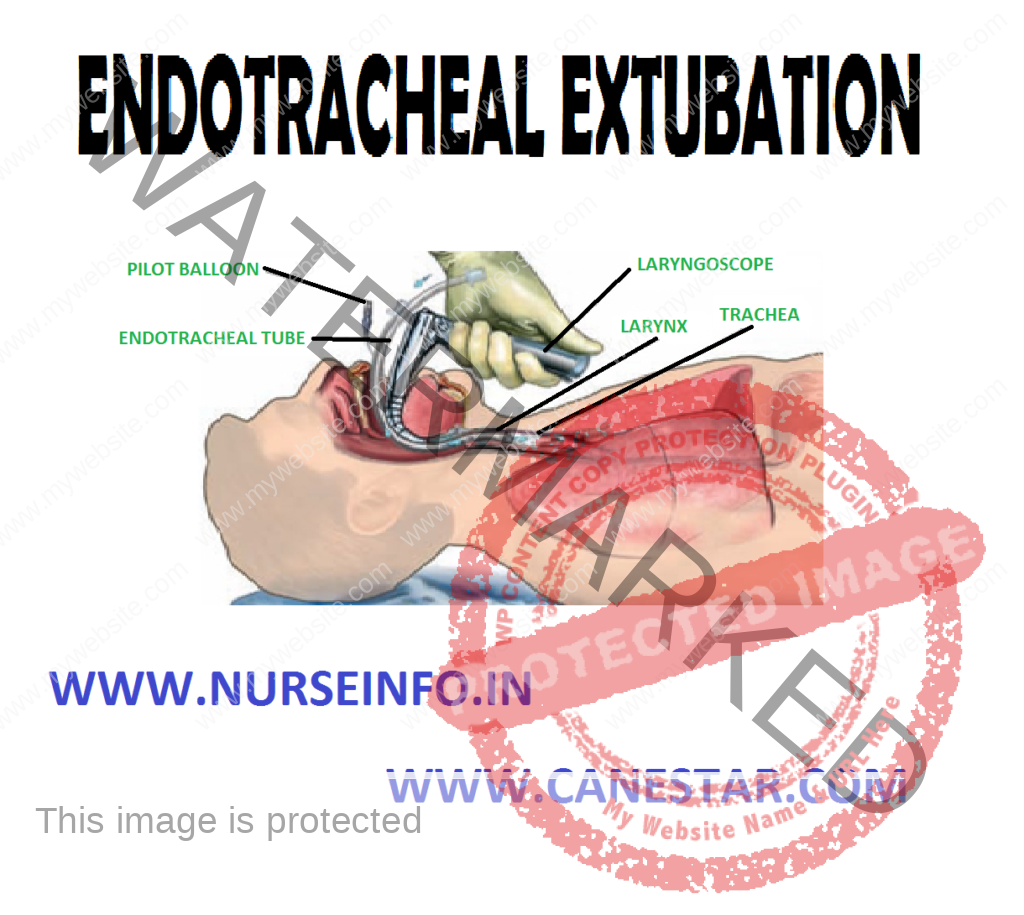
ENDOTRACHEAL EXTUBATION – Objective, Assessment Phase, Precautions, Planning Phase, Client/Family Teaching and Implementation Phase)
OBJECTIVE
To remove either an oral or nasal endotracheal tube after it has been determined that the client can breathe without assistance and that secretions can be removed without an airway in place
ASSESSMENT PHASE
- Can the client ABC value be maintained without assisted ventilation?
- Has the client’s underlying condition improved to the point at which an artificial airway is no longer required?
- Does the client have spontaneous respirations without the assistance of a ventilator?
- Will the client require supplemental oxygen after extubation?
- Are secretions a problem? Will the client be able to cough and clear secretions after the endotracheal tube is removed?
PRECAUTIONS
- Extubations should only be attempted after the client is well-rested, especially in clients who have been intubated for long periods. Extubation may be more successful in the morning than in the late afternoon or evening
- Never remove an endotracheal tube unless the personnel who are trained to reintubate are present. If respiratory failure follows extubation, a patient airway must be re-established
- A suction setup with sterile catheters and gloves must be present during the extubation process to remove secretions in the client’s airway
PLANNING PHASE
- Sterile suction catheter
- Sterile gloves
- Scissors
- Water-soluble lubricant
- Vacuum source lubricant
- Unit dose container of sterile normal saline or 6 ml syringe filled with normal saline stethoscope
- Aerosol setup with supplemental oxygen
Emergency airway box
Manual resuscitator with mask
Laryngoscope and blades
Endotracheal tubes
CLIENT/FAMILY TEACHING
- Discuss the procedure for removing the endotracheal tube
- Describe the suctioning process that will be used concurrently with the extubation procedure
- Encourage the client to cough and breathe deeply, after the endotracheal tube is removed. Describe the benefits of coughing and deep breathing and explain why these procedures will reduce the risk of reintubations
IMPLEMENTATION PHASE
- Elevate head of bed to semi-Fowler’s position or as high as client can tolerate
- Assemble equipment for suctioning as prescribed in previous section on blind endotracheal suctioning
- Assemble equipment to give supplemental oxygen after endotracheal tube is removed
- Remove tape or other means of securing tube in place
- Using sterile technique, suction secretions from the endotracheal tube
- Increase client’s FiO2
- Insert syringe into one way valve in pilot balloon and be prepared to deflate cuff
- Instruct client to breathe deeply. Reinsert suction catheter 1 to 2 inches below end of endotracheal tube, deflate cuff and apply suction while endotracheal tube is removed
- Supplemental oxygen and aerosol should be administered to client as needed
- Tracheostomy tubes are removed in approximately same way as endotracheal tubes are. More attention is given to stoma after tracheostomy tube is removed. Sterile dressing should be applied to stoma after tube is removed. Permanent closure to stoma usually occurs within few days of extubation
- After reoxygenation, encourage client to cough and breathe deeply. Suction oropharynx
- Correctly dispose of tubes, catheters and gloves
Belated Nursing Care
- Encourage client to cough and deep breathly
- Suction is needed to remove secretions from oropharynx and trachea
- Caution: do not leave client unattended. Observe for any signs of respiratory failure and airway obstruction
- Prevention the complication of extubation