NURSING PROCEDURE – DIET FOR PATIENTS (Gastrojejunostomy Feeding, Breastfeeding and Artificial Feeding)
Purpose, General Instructions, Preliminary Assessment, Preparation of Patient and Environment, Equipment, Procedure and After Care
UPDATED 2024
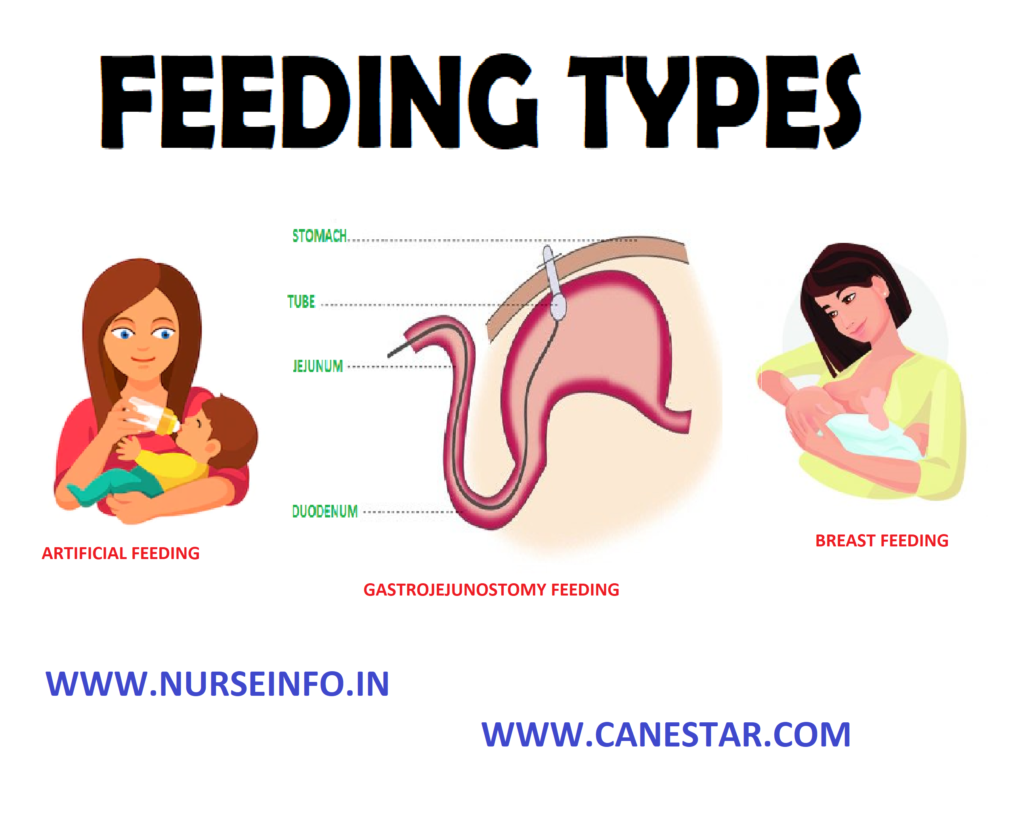
GASTROJEJUNOSTOMY FEEDING
Gastrojejunostomy feeding is defined as enteral nutrition is a liquid food preparation directly into the stomach or small intestine via a tube
It is an ideal method of providing nutrition for the person who is unable to swallow food and drink normally but has intact gastrointestinal function
It is the introduction of liquid good through a tube or catheter which the surgeon has already introduced into the stomach through the abdominal wall
Indications
- Tumors or operations on the upper gastrointestinal tract
- Cancer of the esophagus
- Stricture of the esophagus caused by poisoning in case of fistula
General Instructions
- It is essential that the area of the skin around the tube be kept clean and dry
- A water proof ointment such as zinc oxide may be applied around the tube to protect the skin from the irritation of the hydrochloric acid
- Foods given through the gastrostomy tube are some as those given by nasogastric tube and the same amounts are given at the same intervals
Methods of Administration
- Intermittent feeding: given four to six times a day rather the continuously is delivered as a bolus through a longer lumen tube. Volume for formula usually 250-450 ml is placed in a large syringe and inserted into the proximal end of the tube
- Intermittent gravity drip: administration delivers a similar volume 250-450 ml of feeding over 20-30 ml a minute, four to six times a day
- Continuous administration: delivers fluid through a small lumen tube at a constant rate via orogastric and nasogastric routes. The rate of flow is carefully regulated. The nurse should calculate the amount of fluid to be infused during an hour and regulates the infusion pump accordingly
Preliminary Assessment
Check
- The doctors order for specific instruction
- Level of consciousness of the patient
- Self-care ability of the patient
- Mental status to follow instructions
- Articles available in the unit
Operation of the Patient and Environment
- Explain the sequence of the procedure
- Provide privacy
- Arrange the articles at the bedside
- Place the patient in a comfortable position
- Keep the environment clean and tidy
- Keep ready with feed to be given
Equipment
A clean tray containing
- A funnel, rubber tubing, glass connection screw and a clamp
- A glass of drinking water
- Required amount of fed, temperature 100 degree F
- Sterile lubricant to protect surrounding area
- Sterile dressing and forceps in a dressing tray
- Medicine as per odor
- Kidney tray
- Many tailed binder if required
- Mackintosh and towel
- Stethoscope
- Syringe
Procedure
- Wash hands thoroughly
- Place the mackintosh or towel; clean the surrounding area of the opening. Cover the wound with sterile piece of gauze
- Unscrew the clamp from the gastrostomy tube and attach the funnel and rubber tubing; keep the tube pinched to prevent air from setting in
- Aspirate the gastric contents by attaching a syringe
- Pour some clean water into the funnel and lower a little to let our air
- Then pour the feed before the funnel is empty
- If any medicines are ordered, these are given after feed
- Give water after giving medicines
- Disconnect the tabbling and funnel
- Clean and apply sterile instrument around the wound, dress it with sterile dressing and apply the binder
After Care
- Remove the Mackintosh and towel
- Position the patient comfortable
- Secure the tube with plaster
- Replace the articles to utility room
- Hand wash
- Record the procedure in nurse record sheet
BREASTFEEDING
Breastfeeding is the best food for the baby. It’s not only gives nourishment but also suffice the baby’s emotional needs.
Advantages
- It is the best natural food for the baby
- It fully meets the nutritional requirement of the infant and promotes optimal growth
- It protects the baby from the infections
- It satisfies the sucking reflex of the child
- It is always clean and sterile
- It is available at the correct temperature and requires no preparation
- Lactoferrin present in the breast milk inhibits the growth of bacteria
- Gastrointestinal disturbances are less in breast fed, children, due to presence of lactobacillus fibrous
- It creates bonding between the mother and child
- It helps parents to space their children
- It reduces infant mortality rate
- It helps in involution of the uterus
- It gives baby a sense of security
Contraindication for Breastfeeding
Mother
- Breast diseases e.g., mastitis, breast abscess
- Cardiac diseases and active tuberculosis
- Infectious diseases
- Mental illness of mother
- Unconscious mother
Baby
- Babies with cleft lip and cleft palate
- Premature and sick babies who have poor sucking reflex
- Oral thrush
Breastfeeding Methods
General Instructions
- Mother should keep her body clean and wear clean cloths
- Before each feed, clean the breasts and hands of the mother
- Mother should be in comfortable position during feeding
- Hold the nipple between index and middle finger
- Feed the baby on demand; it helps the baby to gain weight
- Feed the baby for minimum 10 minutes on each breast
- Instruct the mother to feed the baby even when the child is ill
- Burping should be done after each feed to expel the air from the baby’s stomach
- When the baby is 4 to 6 months old start weaning, because, mother’s milk is not sufficient to sustain growth after 6 months of age
- If the baby’s napkin is wet, dirty, change the napkins and cloths before each feeding
- Weigh the child every month and record it
- Teach the mother to have adequate rest to avoid tension, fatigue and stress
ARTIFICIAL FEEDING
Artificial feeding is given to infants instead to the breast milk. Breast milk is often substituted by cow’s milk. The cow’s milk is substituted by dried milk, evaporated milk, etc.
Difference between human’s milk and cow’s milk
Human – carbohydrate (7%), protein (1.5%) and fat (3.5%)
Cow – carbohydrate (4%), protein (4%) and fat (4%)

Preparation of formula
The milk formula should be planned to meet the nutritional requirement of the infant which is based on his age and weight
Caloric requirement: 110 calories per kg of baby weight
Fluid requirement: 165 ml per kg of baby weight
Milk requirement: 100 to 130 ml per kg of body weight
Number of feeds in 24 hours: 7 feeds
Time interval between each feed: 2-3 hours
Preparation of Milk Formula for a Day
Take 460 ml of milk, 140 ml of water and add 9 teaspoonful of sugar and boil it and keep it in the refrigerator, for each feed, take 85 ml of milk, ward it and feed the baby
Different Ways of Feeding in Infant
- By using the feeding bottle and teat
- By nasal tubes
- By belcroy feeder
- By dropper
- By using spoon
General Instructions
- Plan the formula according to the nutritional requirement of the baby
- The feeding bottle, teat and other articles used for the feeding should be sterile
- The milk feed should be warm
- The mother and the child should be in a comfortable position
- Ensure a slow and steady flow of milk by making a hold in the teat neither too big nor too small
- Change the napkin before the feed, if it is wet or soiled
- The feeds should be given at regular intervals
- The mother should wash her hands thoroughly before preparing the feed and feeding the child
- Offer a small quantity of water at the end of each feed
- Never pinch the baby’s nose to make him to open his mouth instead press his cheeks
Preliminary Assessment
Check
- The doctors order for any specific instructions
- Plan the formula according to the nutritional needs of the infant
- Time at which the last feed was given
- General condition of the baby
- Baby’s ability for sucking
- Articles available in the unit
Preparation of the Infant and the Environment
- Arrange the articles at the bedside
- Provide privacy
- Change the napkin if it is wet
- Bath the baby in necessary
- Keep the feeding bottle ready
Equipment
A tray containing
- Mackintosh and towel
- Baby dress and napkin
- Feeding bottle and teat in a sterile container
- Required amount of feed (sterile)
- Sterile water in a bottle
- A piece of clean towel or flannel
- Gown and mask for the nurse
Procedure
- Wash hands thoroughly
- Hold the baby in a position similar to one used for breastfeeding
- Check the temperature of the feed by dropping few drops on the inner aspect of the wrist joint
- Hold the bottle in an angle of 45 degree and bring the teat to the lips and then into the mouth of the baby
- Take care to keep the teat filled with milk throughout the feeding
- Break the wind (burping) in between the feeds
- When the feed is finished, give sterile water to the baby
After Care
- Keep the baby on the shoulders and pat over his back
- Wipe the face
- Remove the towel and lay the baby in the cradle
- Replace the articles in the proper place after cleaning
- Wash hands
- Record the procedure in the nurse’s record sheet
DIET (NUTRITION) FOR SICK PATIENTS
INSERTION OF SENGSTAKEN – BLAKEMORE
NURSING PROCEDURES LIST CLICK HERE

