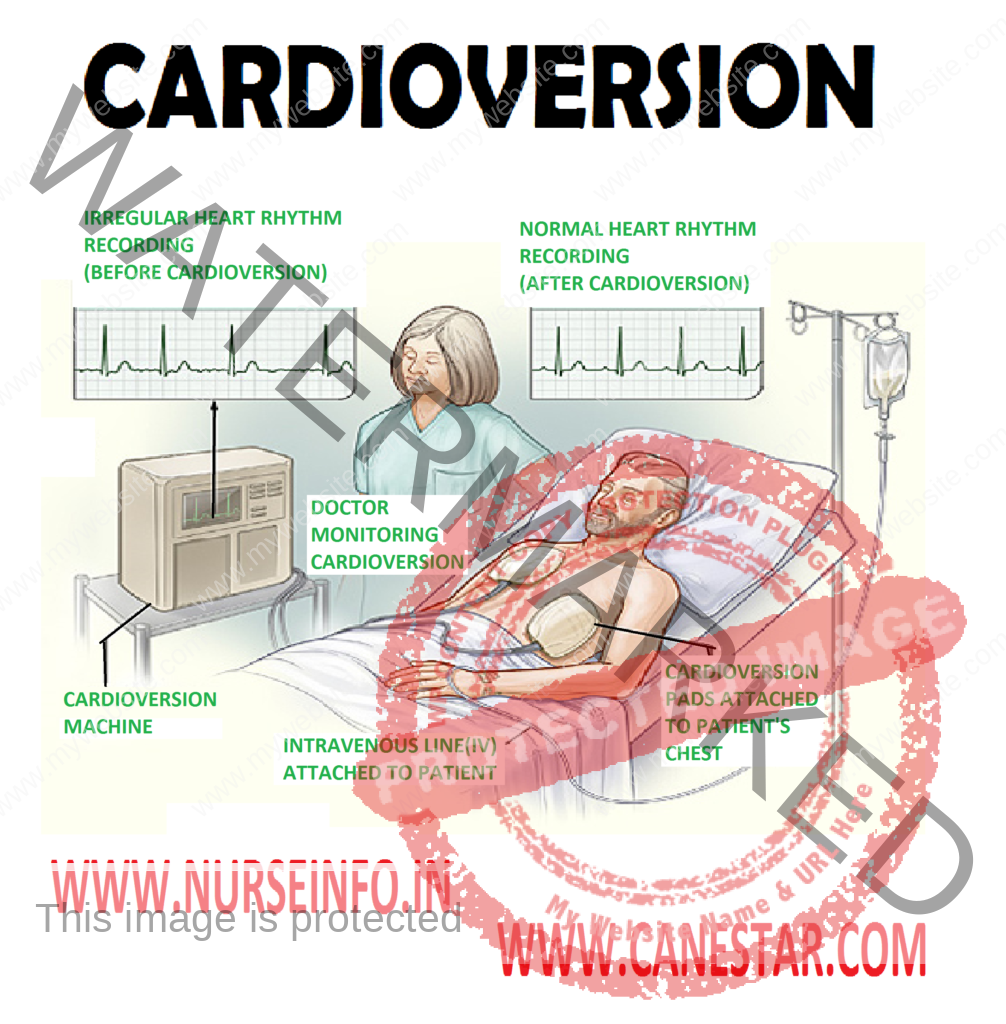
CARDIOVERSION – Definition and Types
Cardioversion is the use of electrical energy to convert a cardiac dysrhythmia, other than ventricular fibrillation, to one that is more hemodynamically stable, preferably a sinus rhythm. Defibrillation generally applies to unsynchronized electrical counter shock during a ventricular fibrillation. It is most effective when the myocardial cells are not anoxic or acidotic. Therefore, defibrillation should ideally be performed within 15-20 seconds of the onset of dysrhythmia. Defibrillation is accomplished by the passage of direct current (DC) electrical shock through the heart that is sufficient to depolarize the cells of the myocardium.
DEFINITION
Cardioversion is a medical intervention used to normalize an abnormal heart rate that occurs in atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia. In these conditions, the heart rate exceeds 100 bpm and is irregular. The condition can be episodic and indicates an underlying heart condition such as hypertension, cardiomyopathy, etc
The subsequent repolarization of myocardial cells will allow the SA node to resume the role of the pacemaker. The output of the defibrillator is quantified in joules or watts per second. The recommended energy for initial shock defibrillation is 200 joules with a second shock of 200-300 joules if defibrillation unsuccessful. High doses of electricity damage thus the lowest effective output is the one with which to start.
CARDIOVERSION TYPES
Electrical cardioversion refers to administration of therapeutic dosage of electric current in a specific moment of the cardiac cycle. The timing is important to avoid ventricular tachycardia. This is a scheduled procedure performed on an out-patient basis on patient who has a history of episodic atrial flutter or atrial fibrillations. Electric current is administered using pads that are placed on the chest or on the chest and back. They are held in place with the help of saline based gel. The cables are connected to machine that generates shocks and displays the cardiac rhythm. The patient is given sedatives to make the entire procedure more tolerable. Electrical cardioversion can at times be used as a lifesaving intervention in emergencies like ventricular tachycardia.
Pharmacological cardioversion entails the use of antiarrhythmic drugs to restore normal heart rate. Sodium channel blockers, beta blockers, potassium channel blockers or calcium channel blockers are the drugs used. All these drugs act to reduce the conductivity of the heart muscle which in turn reduces the heart rate. This is a good alternate in patients with fibrillation of recent onset.