MYELOGRAPHY – Definition, Purpose, Indications, General Instructions, Client Preparation, Procedure and After Care
NURSING PROCEDURES LIST CLICK HERE
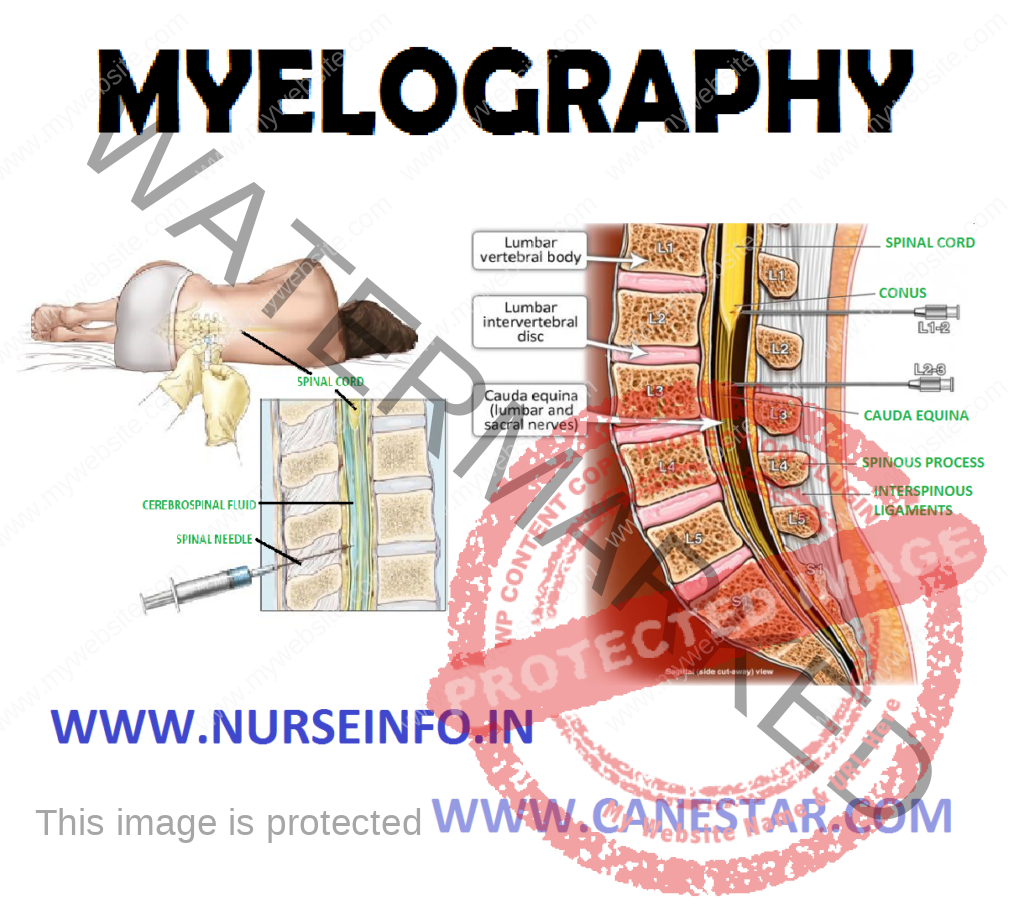
Myelography or myelogram is an X-ray of the spinal subarachnoid space taken after an opaque or air is injected into the spinal subarachnoid space through a spinal puncture. It is also a diagnostic procedure used to visualize the lumbar, thoracic or cervical areas or whole spinal axes for diagnosis of a spinal tumor, a herniated intervertebral disc or a ruptured disc
DEFINITION
Myelography is an X-ray examination of the spinal subarachnoid space taken after an opaque medium or air is injected into the spinal subarachnoid space through a spinal puncture. It shows any distortion of the spinal cord or spinal dural sac caused by tumors, cysts, herniated intervertebral discs or other lesions
PURPOSE
- To identify space-occupying lesions of the spinal cord
- To help diagnosis a herniated nucleus pulposus
- To diagnose intramedullary tumors
- To identify the traumatic lesion and cysts of the vertebrae or the spinal cord
INDICATIONS
- Spinal cord tumors
- Traumatic lesions of the spinal cord
- Herniated intervertebral disc
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS
- The client should be prepared physiologically and psychologically
- Strict aseptic technique should be followed throughout the procedure
- The client should be informed that the X-ray table may be titled in varying positions during the study
- The commonly used dyes are mertrizamide (amipaque) and iophendylate (pantoopaque) so the sensitivity should be checked
- Instruct the client to remain supine for 12 to 24 hours after the procedure
- Inform the client that the procedure is done in X-ray department
CLIENT PREPARATION
- Explain the procedure to the patient and relatives
- Obtain informed consent
- The meal that would normally be eaten prior to the procedure is omitted
- The client may be given a light sedative to help cooperate
- Sensitivity test for the dye must be checked
PROCEDURE
- Place the client on the X-ray table
- Position the client for lumbar puncture
- LP needle is inserted L4-L5
- Approximately 10 ml of CSF is removed
- Water soluble nonionic contrast medium is then injected
- The table is titled to allow the column of the dye to move up and down within the subarachnoid space
- By minimal changes in position of the table and patient, various regions of the spine are screened and films taken at appropriate levels
AFTER CARE
- Keep the client strict bed rest
- Position the client’s head elevated 30 degree
- Check the neurological and vital signs
- Encourage more oral fluids
- Provide light soft diet if no nausea and vomiting
- Mild analgesics may be given if headache persists
- Check the client’s ability to void
- Observe for fever, stiff neck, photophobia or the signs of chemical or bacterial meningitis