CORD BLOOD BANKING – TRANSFUSION, USES, BANKING, INDICATIONS, ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF CORD BLOOD BANKING
CORD BLOOD TRANSFUSION
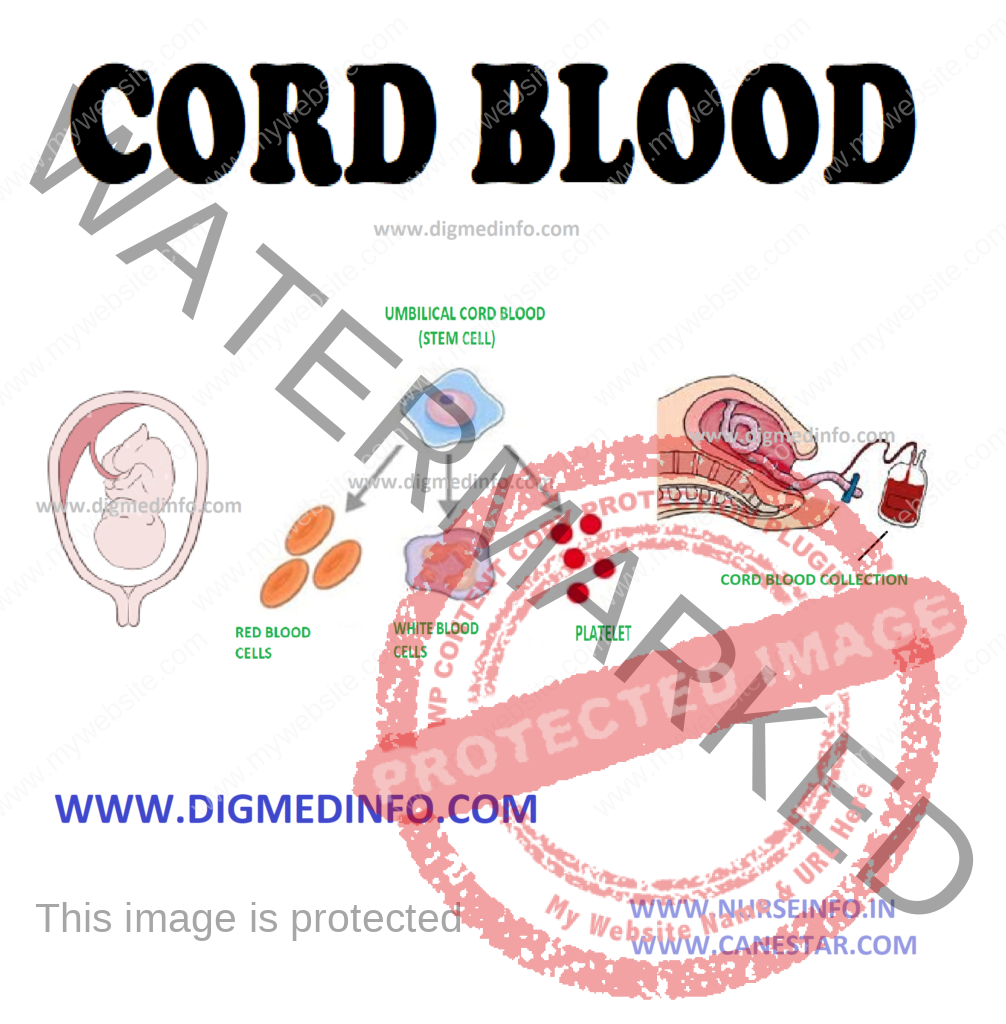
Cord blood is the blood obtained from placenta and in the attached umbilical cord. Sources of stem cells include bone marrow, peripheral blood, umbilical cord blood, fetal organs and artificially produced human embryos in vitro.
Cord blood is a rich source of multipotent stem cells. They are less likely to mount immunological reactions. Cord blood stem cell infusion is becoming more popular.
Use of blood collected from the umbilical cord after delivery as a source of stem cells has become an established procedure within the past 15 years. Cord blood contains large number of granulocyte-macrophage progenitor stem cells, sufficient enough to re-populate marrows of irradiated subjects. This has paved the way for organized cord blood banking. There are several blood banks undertaking storage and delivery of cord blood, all over the developed countries. There are a few privately-owned cord blood banks in the world. Cord blood can be cryopreserved in the viable state for many years. The services provided include:
1. Use of cord blood as a source of stem cells and
2. Preservation of the cord blood indefinitely for long periods, for use in the same individual if a need for stem cells arises. The donor is charged for this service.
Uses of Cord Blood
1. Allogenic transplant
2. Autologous transplant
3. As a source of multipotent stem cells for reconstitution and repair of damaged tissues such as the heart, after myocardial infarction.
The immunological properties of cord blood stem cells differ from those of adult marrow or peripheral blood.
Cord blood contains a higher proportion of T-cells expressing (C D 45 R A +/ C D 45 R A O–) and CD 62 L+. These cells are immunologically naïve and therefore graft versus host disease is less common.
The chemokine receptor C C R5 expressed by Th-1 T lymphocytes is less abundant in cord blood T-cells compared to adult T-cells.
Cord Blood Banking
Pregnant women are recruited as donors after obtaining informed consent, and excluding common communicable diseases. Blood is collected from the placental side of the severed umbilical cord either in utero before the delivery of the placenta or ex-utero after its delivery. Long-term storage is done under temperatures below –180° C and released for use on demand after proper cross-matching.
Indications for Cord Blood Transfusions
a. Stem cell replenishment in hematological malignancies—acute leukemias, chronic myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome.
b. Non-malignant conditions-aplastic anemia, thalassemias, hemoglobinopathies, immunodeficiency states.
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF CORD BLOOD
Advantages of cord blood are its availability, lower incidence of graft versus host disease (GVHD) and good success rate even if mismatched for two antigens. The waiting period for transplantation is also shorter.
Disadvantages are the higher infection rates with cord blood stem cells, compared to preparations from bone marrow or peripheral blood from adult donors.
Future strategies for improving the service include:
1. Pooling of cord blood
2. Cord blood expansion using cytokines which stimulate stem cell proliferation
3. Combining cord blood and haplo-identical bone marrow transplants
4. Non myeloablative or reduced intensity conditioning regimen.