COLONOSCOPY – Definition, Purpose, Indication, Principle, General Instruction, Preliminary Assessment, Preparation of the Article, Preparation of the Patient, Procedure, After Care and Complication
DEFINITION
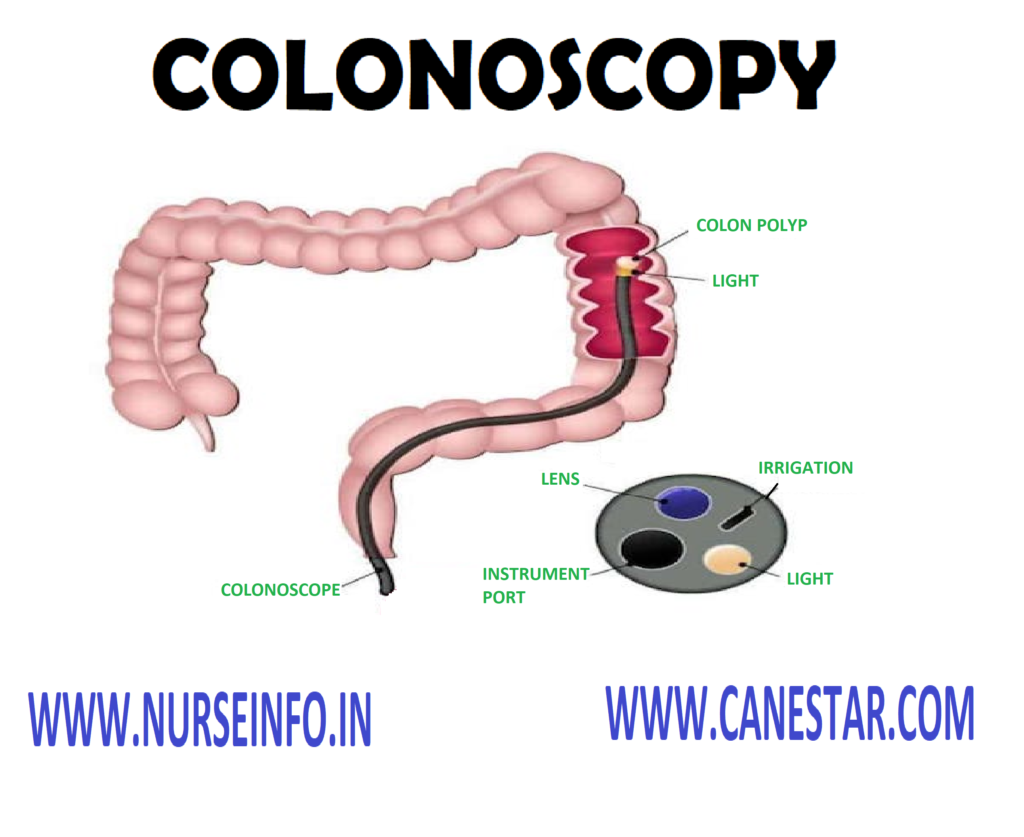
It is a diagnostic procedure which provides visualization of the lining of the large intestine with the help of flexible endoscope.
PURPOSE
Diagnostic Purposes
- To detect colon cancer or polyps
- To detect inflammation and disease of bowel
Therapeutic Purposes
- To remove the polyps
- Detection and prevention of colorectal cancer
- To treat bleeding or stricture
INDICATION
- Unexplained constipation/diarrhea
- Rectal bleeding, lower abdominal pain
PRINCIPLE
- A thorough knowledge about the anatomy and physiology of the GI tract
- Mental and physical preparation of the patient facilitates introduction of the tube
- Systematic way of functioning saves, time, energy and material
- Any unfamiliar situation procedure fear and anxiety
GENERAL INSTRUCTION
- Explain the procedure to the client to win his confidence and cooperation
- Limit the intake of fluids for 24 to 72 hours before the examination
- Fleet saline enema should be given until the return is clear
- Lavage solutions are used for effective cleansing of bowel
- Instruct the patient not to take routine medication when lavage solution is ingested
- Advise the diabetic patient to consult his/her physician about medication adjustment
- Instructing all the patients especially elderly to maintain adequate fluid, electrolyte and caloric intake
- NSAIDs must be discontinued before the test and for 2 weeks after the procedure
- The patients having cardiovascular disease require careful cardiac monitoring during the procedure
- Colonscopy cannot be performed if there is a suspected colon perforation, acute severe diverticulitis
- The patients taking heparin must consult physician for specific instruction
PRELIMINARY ASSESSMENT
- Identify the patient name, age, sex, diagnosis, ward and bed numbers
- Check the doctor’s order for specific precaution
- Check the general condition of the patient
- Check for any lesion on the rectal area
- Check the consciousness and ability to follow the instructions
- Check the articles available in the unit
- Check the purpose of the procedure
- Check the medical order for the collection of specimen
PREPARATION OF THE ARTICLE
- Colonoscope
- Draping sheet
- Lubricant
- Cotton swabs
- Gloves
- Emesis basin
- Toilet tissue paper
- Kidney tray and paper bag
- Biopsy forceps
PREPARATION OF THE PATIENT
- Explain the procedure to the patient
- Provide privacy with curtains
- Cover the patient with sheet or bath blanket
- The patient receivers NPO after midnight before the test
- Place the patient in a left lateral position
- Keep the entire article on the bedside and check the articles for good working condition
- Remove the bottom garments or raise it up above the waist level
- Get the written consent from the client
PROCEDURE
- The patient assumes left lateral position. Ask him to relax as much as possible. The client is usually given (IV) sedation with valium, Demerol. The lubricated colonoscope is inserted into the anus. A small amount of it is instilled to help the physician visualize the bowel lumen. When the colonoscope reaches the sigmoid junction, the client may move to the supine position making it easier to advance the colonoscope pass the splenic flexure. During the test, encourage the client to relax. Monitor the vital signs throughout the procedure watching for a vasovagal response reaching to hypotension and bradycardia
AFTER CARE
- Place the patient in a comfortable position
- Monitor the vital signs
- Assess for the signs of perforation
- Administer the IV fluids with sedation
- Client may develop nausea which may dictated with IV antiemetic
- Recording and reporting (time, date, patient response, complication, if any)
COMPLICATION
- Bleeding
- Intestinal perforation