CANDIDIASIS – General Characteristics, Diagnosis and Treatment
General Characteristics
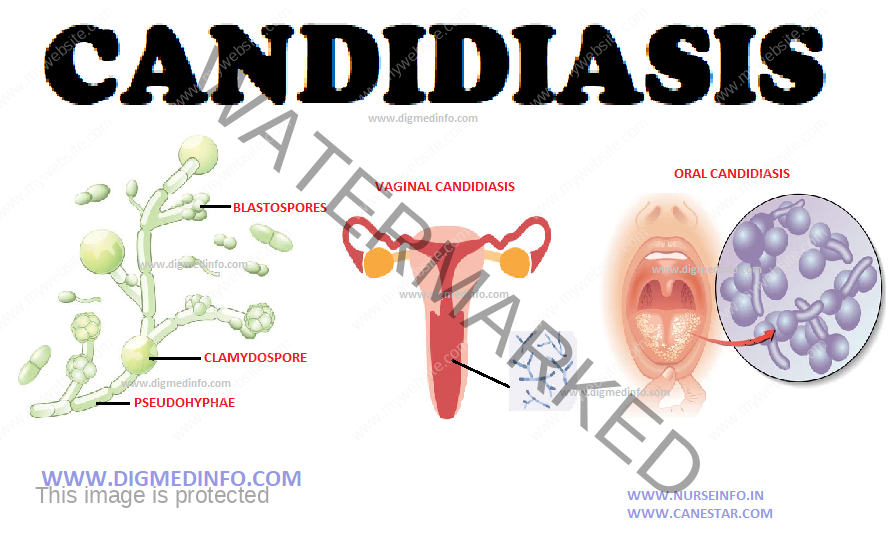
Candida albicans is a common inhabitant of the oropharyngeal, genital and intestinal cavities of man. Candidiasis is infection by Candida albicans. In most of the cases it remains as a local infection affecting the skin or mucous membranes of the mouth or genitalia. In the mouth it presents as oral thrush which is seen at the extremes of ages, those on antibiotic therapy or in immunosuppressed individuals. In the genitalia it usually presents as vulvovaginitis in diabetic women who are not well-controlled. Cutaneous candidiasis usually affects the intertriginous areas.
Systemic candidiasis occurs in immunocompromised individuals and in drug addicts who share needles. The fungus becomes invasive and spreads through the blood stream to produce several lesions.
1. Localized lesions: Urinary tract, liver, heart valves, meninges and peritoneal cavity.
2. Widely disseminated: Associated with septicemia (candidemia). In disseminated candidiasis also the main targets of attack are the kidneys, brain, liver, gastrointestinal tract, eye (endophthalmitis) and heart valves.
Extensive, recurrent and persistent oropharygeal and esophageal candidiasis is a common AIDS associated infection.
Diagnosis
The organism can be demonstrated microscopically by examining samples from local lesion. In tissues, PAS staining or methenamine silver staining reveals the organism.
The fungus can be grown in Sabouraud’s medium. Antibodies to Candida can be detected by ELISA or immunodiffusion. The candidal antigen can be demonstrated by ELISA or radioimmunoassay.
Treatment
Amphotericin B, fluconazole, ketoconazole and itraconazole are all effective in appropriate dosage to control the systemic infection. Local surgical therapy should be aimed at removal of the source of infection.
Dose: Amphotericin B up to 50 mg/day IV for 1-2 weeks and more.
Fluconazole 400 mg/day.
Ketoconazole 400 mg/day for several weeks.
Itraconazole 200-400 mg/day.
Itraconazole and fluconazole are less adrenosuppressive compared to ketoconazole. Superficial skin and mucous membrane lesions respond well to nystatin ointment or nystatin mouth washes. Fluconazole given orally is very effective to cure vaginal candidiasis.