BLADDER IRRIGATION
Bladder irrigation is a medical procedure commonly used to flush out the bladder with a sterile solution. This procedure is typically performed for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes and is carried out by healthcare professionals.
Here are some common reasons for bladder irrigation:
- Hematuria (Blood in the Urine): Bladder irrigation may be used to treat or prevent blood clot formation in the bladder in cases of significant hematuria. The irrigation helps remove clots and blood from the bladder, reducing the risk of obstruction.
- Postoperative Care: After certain urological surgeries, such as transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) or bladder tumor removal, bladder irrigation may be performed to prevent blood clot formation and ensure clear urine drainage.
- Infection Control: Bladder irrigation with an antimicrobial solution may be used to manage or prevent urinary tract infections (UTIs) in some cases.
- Chemotherapy or Immunotherapy: Bladder irrigation may be employed in the treatment of bladder cancer. Medications, such as chemotherapy or immunotherapy agents, can be instilled into the bladder and then drained out to target cancer cells.
- Diagnostic Procedures: Bladder irrigation may be part of diagnostic procedures, such as cystoscopy, to provide clear visualization of the bladder lining.
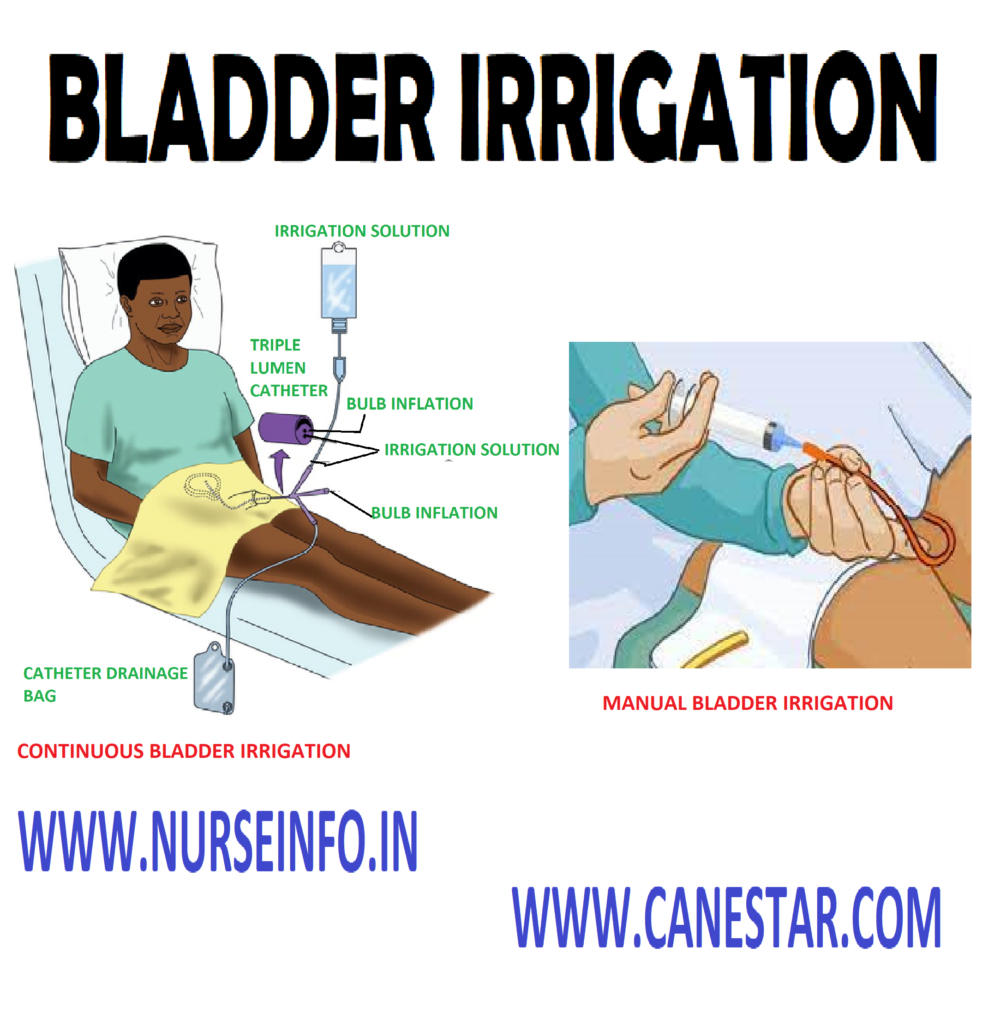
The procedure involves the insertion of a catheter into the bladder through the urethra. A sterile irrigation solution is then introduced into the bladder, and the fluid is allowed to drain out, carrying away debris, blood, or other substances. The process is typically repeated until the drained fluid is clear.
Bladder irrigation requires careful monitoring to avoid complications, and it should only be performed by trained healthcare professionals. Patients undergoing bladder irrigation may experience temporary discomfort, urgency, or increased frequency of urination.
Bladder irrigation or wash is defined as washing of the urinary bladder by directly a stream of solution into the bladder through the urinary meatus by means of a catheter tubing and funnel
Purpose
- To cleanse the bladder from decomposed urine bacteria, excess mucus and pus
- To medicate the lining of the bladder of antiseptic irrigation
- To prepare the bladder for surgery as a preoperative measure
- To promote healing
- To relieve congestion and pain in case of inflammatory conditions of cystitis
- To arrest bleeding and prevent clothing of blood
Solution Used
- Normal saline 0.9%
- Boric acid solution 2%
- Sterile water
- Acetic acid 1:4000 to treat pseudomonas infection
- Sodium nitrate 1:8000 to prevent clot formation
- KMO4 1:5000 – 1:10,000
- Acriflavin 1:10,000
- Silver nitrate 1:5,000
- Mercury compounds in low concentration
General Instructions
- The temperature of the solution needed for cleaning purpose body temperature in enough
- The temperature of the solution needed for therapeutic purposes ranging from 100-110 degree F
- The maximum amount of solution used for cleaning is 2 pints and also depends on the patient’s condition
Methods of Administration
- Funnel and tubing method (open method)
- Irrigation can, rubber tubing and Y connection
- Asepto syringe (open method)
Preliminary Assessment
Check
- Doctors order for specific precautions and instructions
- General condition of the patient
- Diagnosis of the patient
- Self care ability of the patient
- Mental status to follow instructions
- Articles available in the unit
Preparation of the Patient and Environment
- Explain the sequence of the procedure
- Arrange the articles at the bed side
- Provide privacy
- Place the patient in comfortable position
- Place the Mackintosh under the buttocks
Equipment
Sterile Catheterization Pack
A sterile tray containing:
- Funnel, tubing 3 feet long which fits the connection screw clip and glass connection
- A small mug or pint measures to pour solution
- A sterile pint jug with required solution
- Solution thermometer kept in antiseptic solution in a bottle if available
- Medication if ordered
- Bucket for emptying the return flow
- Litmus paper
Procedure
- Wash hands thoroughly
- Wear gloves and empty the bladder keeping outlet of catheter uncontaminated
- After urine withdrawal, attach glass, connection, tubing and funnel to the catheter
- Place bucket or kidney tray conveniently near the meatus
- Hold the funnel lowered with one hand and with other hand pour 75-100 ml of solution along sides of the funnel
- Raise the tube and keep the funnel 30 cm above bed level
- Never allow the funnel to be empty, lower the funnel and slowly invert in over the bucket
- Repeat procedure until the return flow is clear
- At the end of the procedure, clamp tubing disconnects glass connection, tubing and funnel, gently remove catheter and complete
- In case of self-retaining catheter connect it to the drainage bag
After Care
- Provide catheter care
- Remove the Mackintosh and position the patient comfortably
- Cover the patient with bed sheets
- Replace the articles after cleaning
- Wash hand thoroughly
- Record the procedure and observations in the nurse’s record sheet