ASPERGILLOSIS – General Characteristics and Treatment
General Characteristics
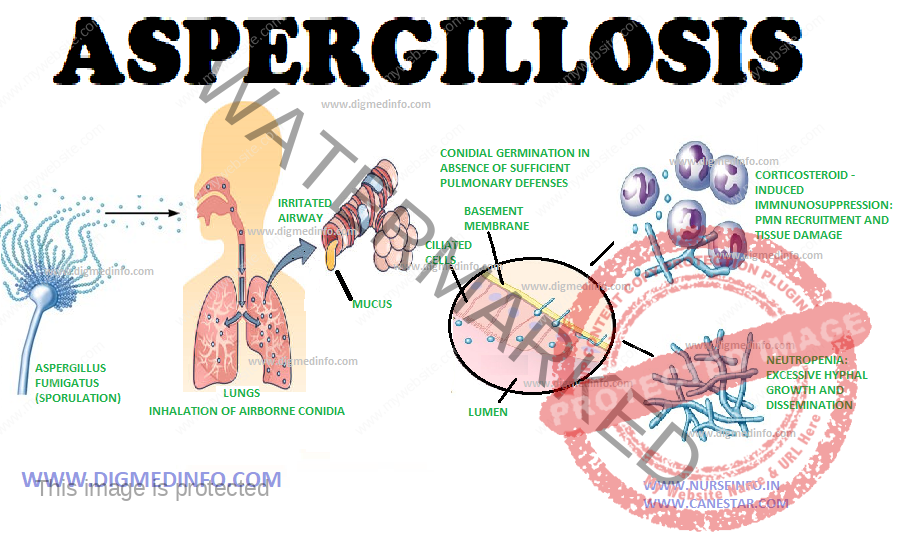
The species of aspergillus pathogenic to man are A. fumigatus, A. niger, A. flavus, A. terrens and A. nidulans. Of these A. fumigatus is most common. Infection occurs when general resistance is lowered or local disease favours superinfection. Aspergillus is very widespread in nature and their spores are found in dust. Both superficial and systemic lesions may develop. The commonest superficial lesion is otomycosis. Systemic infection may be pulmonary or disseminated. Major portal of entry is the respiratory tract.
Pulmonary form: Allergic alveolitis may develop due to inhalation of fungal spores in sensitized individuals. Aspergillus may grow in the bronchi to produce bronchopulmonary disease. The hyphae may obstruct the lumen. Healed tuberculous cavities or other types of cavities may be the seat of colonization by the fungus.
The mycelia grow to form a tangled fungal ball which is recognizable in X-rays (aspergilloma). It may remain asymptomatic or may cause massive hemoptysis. Invasive aspergillosis occurring in immunosuppressed individuals leads to widespread pulmonary necrosis with marked systemic symptoms.
Other sites of lesion are the central nervous system and naso-orbital cavities. Diagnosis can be made by histological demonstration of the fungus and isolation of the organism from the exudates. Since Aspergillus is a common contaminant in respiratory secretions, mere isolation does not prove its pathogenic role. Precipitating antibodies can be demonstrated by gel diffusion test and this test is of great value in diagnosis.
Treatment
Amphotericin B in a dose of 1 mg/kg/day is effective in systemic aspergilloma. Amphotericin B and 5-fluocytosine are effective in CNS disease. The underlying predisposing factor should be attended to. Cavities containing aspergilloma producing intractable hemoptysis have to be removed surgically. Other drugs like clotrimazole which are also effective in vitro are being evaluated. Other drugs effective against aspergillus include oral fluconazole itraconazole, voriconazole and posaconazole. Posaconazole can be given prophylactically against aspergillus and other fungal infections in neutrophilic patients. The dose is 200 mg tds oral. Capsofungin a new antifungal drug effective against aspergillus and other yeast species.