SURGICAL SOAK – Purpose, Preliminary Assessment, Preparation of the Patient, Equipment, Solutions Used and Procedure
Updated 2024
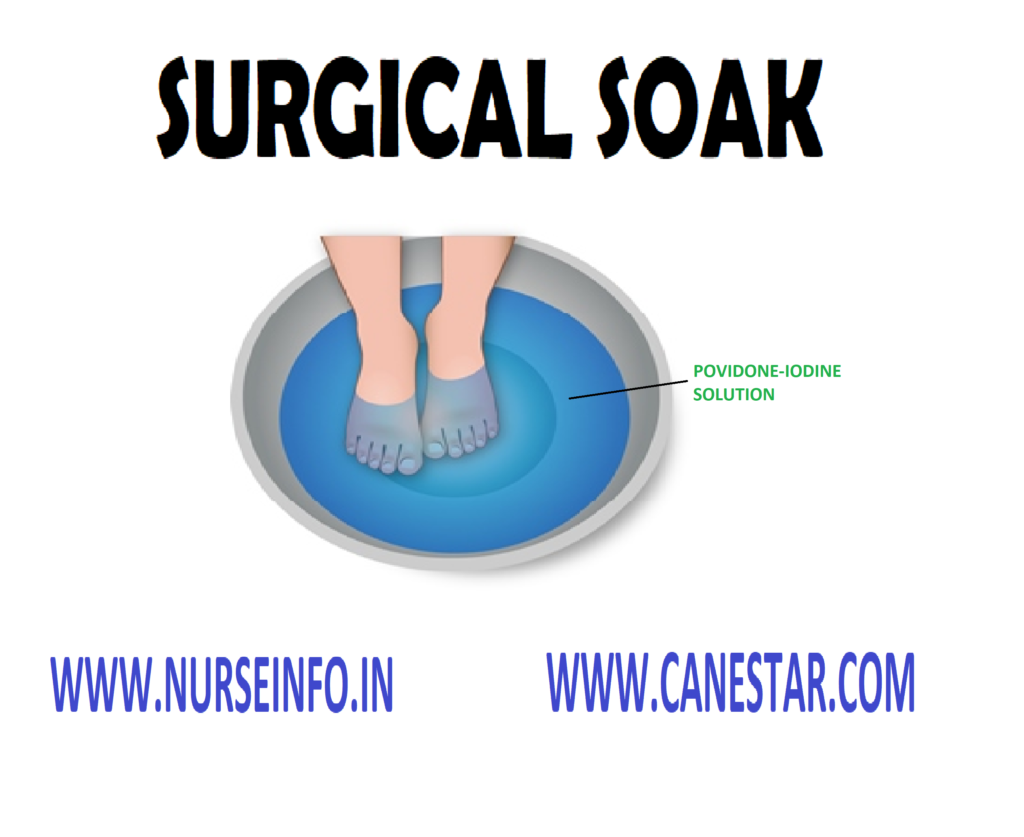
Surgical soak is the submerging or directly immersing a body part or wound in a therapeutic solution using sterile technique
Surgical soak is the local bath of the part of the body such as arm or foot. When there is an open wound moist heat is applied by soaking or immersing the part in sterile warm solution
PURPOSE
- To promote wound healing by increased circulation
- To relieve discomfort and pain
- To relieve congestion and crust formation
- To reduce edema
- To aid cleaning of slough from wounds
- To apply medication to locally infected area
- To make manipulation of painful area easier
- As preparation for surgery, for example, diabetic ulcer foot for skin grafting
NURSING ARTICLES AND PROCEDURES CLICK HERE
PRELIMINARY ASSESSMENT
- Check the general condition of the patient
- Check the physician’s order
- Maintain the desired position
- Provide privacy to the patient
- Check the articles available in the patient’s unit
PREPARATION OF THE PATIENT
- Explain the procedure to the patient
- The dressing change is scheduled for a suitable time
- If the patient is in an open unit the curtains are drawn to ensure privacy
- To incisions should not be referred to as a scar because, for some patients, the term has negative connotations
EQUIPMENT
- Sterile basin or bucket
- Boiled water
- Lotion thermometer
- Normal saline
- Small Mackintosh
- Unsterile K-basin
- Duster
- Sterile pint measure
- A bowl with cotton balls
- Gauze piece, cotton pads
- Gloves, gown mask
- Sponge holding forceps
SOLUTIONS USED
- Water (105 -110 degree F or 40-45 degree celcius)
- Concentrated normal saline
- Potassium permanganate (till turns pink color)
- Dakin’s (Na hypochlorite) solution. Duration: 15-20 minutes
PROCEDURE
- Remove outer dressing as in surgical dressing
- Wash hands
- Check temperature of the water
- Open sterile basin and pour water into sterile basin
- Add prescribed medication with sterile pint measure
- Keep basin on small Mackintosh
- Open dressing pack and remove adherent dressing
- Ask patient to immerse part into basin after checking patient’s tolerance
- Instruct to soak area for 15-20 minutes
- Remove basin and drape wound with sterile cover
- Do dressing
- Record time, type, amount and temperature of solution, duration of wound, drainage or exudates, conditions and cooperation of patient
- Replace the articles
NURSING PROCEDURES LIST CLICK HERE
KEY POINTS TO SURGICAL SOAK PROCEDURE
However, here are some general key points that might apply to such procedures:
- Aseptic Technique: Maintaining aseptic or sterile conditions is crucial during any surgical procedure. This includes the use of sterile solutions for soaking or irrigating to minimize the risk of infection.
- Choice of Solution: The choice of solution for soaking or irrigating depends on the nature of the surgery and the body part involved. Common solutions include saline, antiseptic solutions, or specialized irrigation solutions.
- Temperature Considerations: Ensure that the solution used for soaking or irrigating is at an appropriate temperature. Extreme temperatures can be harmful to tissues, so solutions are typically warmed to body temperature.
- Proper Irrigation Technique: The technique used for irrigation is important. It should be gentle yet effective in removing debris or contaminants. The surgeon or medical professional performing the procedure needs to be skilled in proper irrigation techniques.
- Monitoring Fluid Absorption: In some cases, especially in procedures involving body cavities, it’s important to monitor the volume of fluid used for irrigation to prevent complications such as fluid overload.
- Postoperative Care: After the procedure, postoperative care includes monitoring for any signs of infection, proper wound care, and ensuring that the patient is recovering well.

