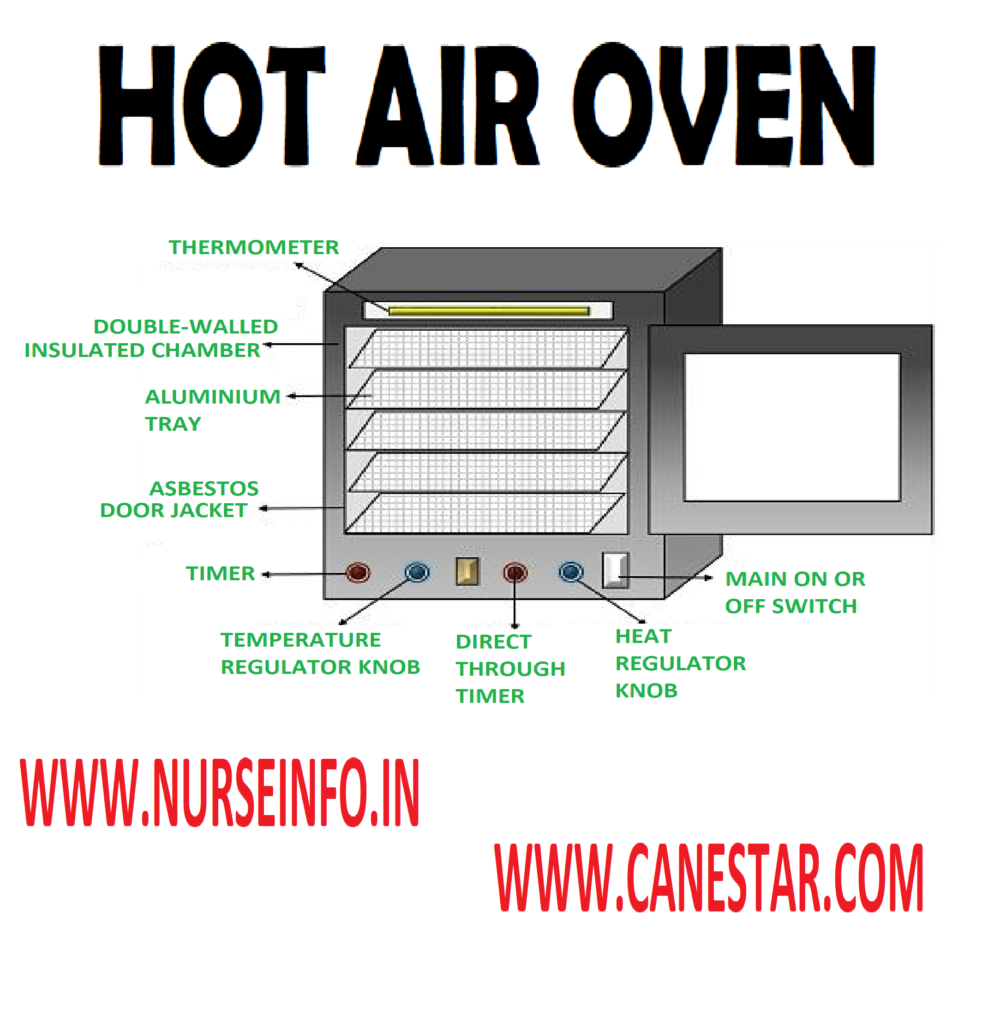
A hot air oven is a type of dry heat sterilization device commonly used in laboratories, research facilities, and industries. It operates by using hot air to achieve high temperatures, effectively eliminating microorganisms and achieving sterilization. Here are key features and uses of hot air ovens:
Features:
- Design:
- Hot air ovens typically consist of an insulated chamber made of metal, with a heating element to generate heat.
- Temperature Control:
- They are equipped with a thermostat or temperature controller to regulate the internal temperature accurately.
- Timer:
- Ovens often include a timer to set the duration of the sterilization cycle.
- Air Circulation:
- Efficient air circulation is important for even heat distribution throughout the chamber, ensuring uniform sterilization.
- Ventilation:
- Some ovens have ventilation systems to release excess moisture during the sterilization process.
Working Principle:
- Heating Element:
- The heating element in the oven generates heat.
- Thermostat Control:
- The thermostat controls the temperature, maintaining it at the desired level for the specified duration.
- Sterilization Cycle:
- Items to be sterilized are placed inside the oven. The sterilization cycle begins when the set temperature is reached.
- Cooling:
- After the sterilization process, the oven may include a cooling phase before the items can be safely removed.
HOT AIR OVEN
High temperature and comparatively long exposure times are required for hot air oven. Various types of powders, glass materials, etc. are sterilized by this method
Mechanism of Hot Air Oven
- It works on the principle of sterilization by dry heat
Temperature: 160 degree celcius
Time: one hour
- Articles sterilized include glassware, forceps, scissors, scalpels, syringes, liquid paraffin and dusting powder
Advantages
- All types of microorganisms including spores are killed by this method
- It is safest method of sterilization
Disadvantage
- It is costly method of sterilization
General Instructions
- Glassware should be perfectly dry before placing in the oven
- Oven must be allowed to cool down for 2 hours before door is opened after sterilization
- It should not be overloaded
- Articles should be arranged in such a manner that free circulation ofd air is possible
Uses:
- Laboratory Sterilization:
- Hot air ovens are commonly used in laboratories for sterilizing glassware, instruments, and other equipment that can withstand dry heat.
- Pharmaceutical Industry:
- In pharmaceutical manufacturing, hot air ovens are used for sterilizing equipment and containers used in drug production.
- Dental Clinics:
- Dental instruments that are heat-resistant can be sterilized in hot air ovens.
- Research Facilities:
- Research laboratories use hot air ovens for sterilizing media, instruments, and other materials.
- Textile Industry:
- Some textile materials and products may be subjected to hot air oven treatment for sterilization.
Advantages:
- Dry Sterilization:
- Hot air ovens provide dry heat sterilization, which is suitable for items sensitive to moisture.
- Ease of Use:
- They are relatively simple to operate and do not require water or other chemicals.
- Uniform Heating:
- Efficient air circulation ensures uniform heat distribution, contributing to effective sterilization.
- Economical:
- Hot air ovens are generally cost-effective compared to other sterilization methods.