FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION BIOPSY/CYTOLOGY – Technique, Equipment Needed, Procedure, Variation in Technique and Indications
Fine needle aspiration biopsy cytology (FNAB/FNAC) diagnosis has important applications in surgical practice.
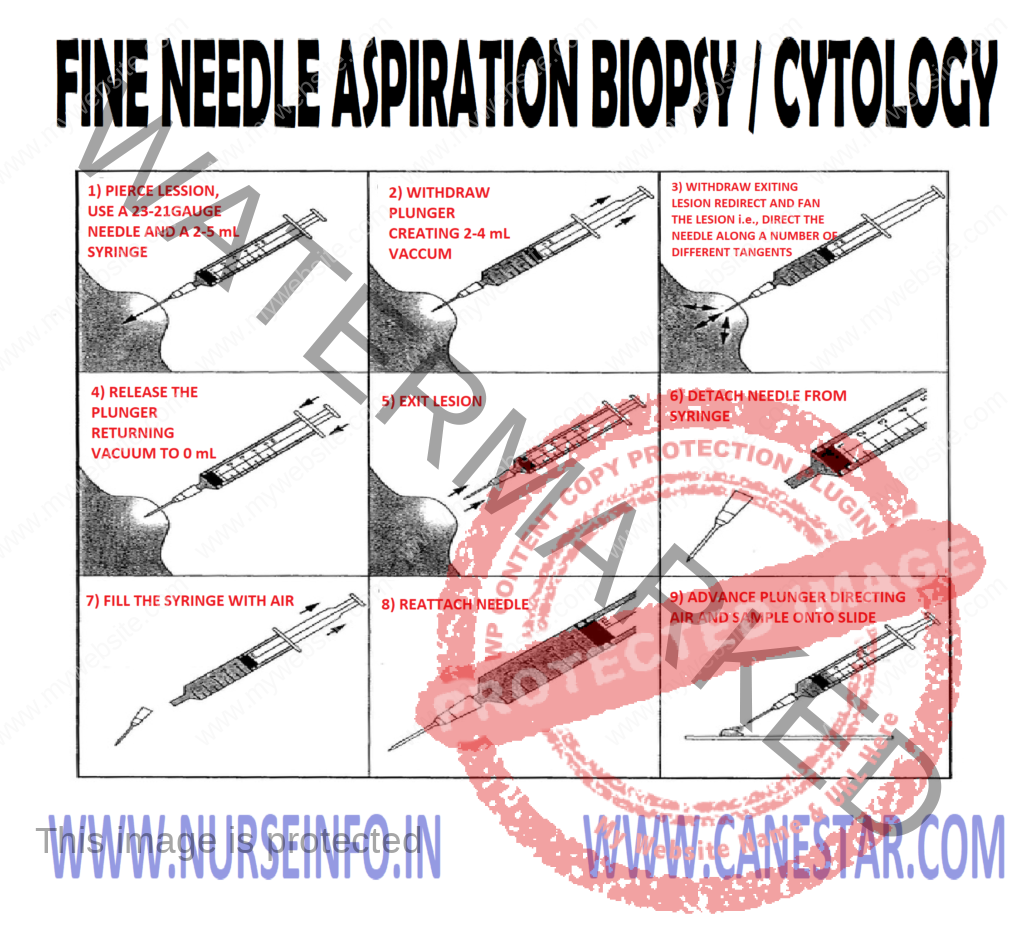
TECHNIQUE
Anesthesia: usually anesthesia is not required, sometimes local anesthesia/general anesthesia may be required for image intensification, e.g. renal and vertebral puncture.
EQUIPMENT NEEDED
- A 20 ml syringe
- Long needle for deep aspiration (spleen, liver or kidney)
- Stronger needle (1-1.2 mm diameter) with trocar for skeletal puncture
- Fine (23 and 26 gauge) needles for small breast cyst or for the puncture of abdominal organs
PROCEDURE
- Explain the procedure to the patient
- Cleanse the skin with an antiseptic solution and drape
- Insert the needle delicately into the lesion by an oblique tract, perceiving the tissue texture on entry and the piston and keep it steady. With suction in place pass the needle gently through the lesion in three or four directions. Then release the piston gently to release the suction, and withdraw the needle
- Apply pressure over the puncture site with a cotton wool ‘ball’ for 5 minutes
- Detach the needle from the syringe and draw the air into the syringe; contents of the needle bore are blown onto dry and clean microscopic slide
- Lightly spread the tissue juice and tumor fragments with the needle point as for bone marrow
- Staining
Immediate air-drying by waving the slide. This may be improved by hot air from hair-dryer or hot light bulb. Then the smear is fixed in methanol for 5 minutes and stained with Romanovsky stain
Immediate wet fixation of smears with ethanol and staining by Papanicolaou or hematoxylin and eosin ( H and E)
When immediate diagnosis is required preoperatively, dick quick staining method is valuable
VARIATION IN TECHNIQUE
- For splenic, hepatic and abdominal puncture, the clotting factors must be normal and local anesthesia employed. Aspiration is performed swiftly, with the patient holding breath after deep inspiration
- For skeletal puncture, it is not necessary to penetrate cortex. Primary and secondary bone tumor tissues may lie periosteally. A glancing aspiration on a skeletal surface frequently gives cells
INDICATIONS
- Breast
Carcinoma breast to confirm the diagnosis
Treatment of breast cyst
Inflammatory breast lesion
Impalpable mammographic abnormality
- Lymph node: lymphadenopathy
- Salivary swellings
- Thyroid swelling (goiter)
- For liver pathology in place of the needle biopsy
- Abdominal and retroperitoneal mass
- Pancreas: to distinguish carcinoma from chronic pancratitis, FNAB/C may be done preoperative as a guided procedure using endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancratography (ERCP), ultrasound or angiography
- Soft tissue lesion, e.g. soft tissue sarcoma
- Bone tumors
- Prostatic lesion
- Testicular lesion
- Cervical cysts, e.g. thyroglossal, branchial and desmoid cyst
Advantages: easy, simple and less painful technique. The patient’s compliance is more, so easily repeated. It is more convenient for a busy surgical practice and can be performed in the outpatient clinic.