ENDOMYOCARDIAL BIOPSY – Purpose, Findings, Interfering Factors, Client Preparation, Procedure, After Care and Complications (NURSING PROCEDURE)
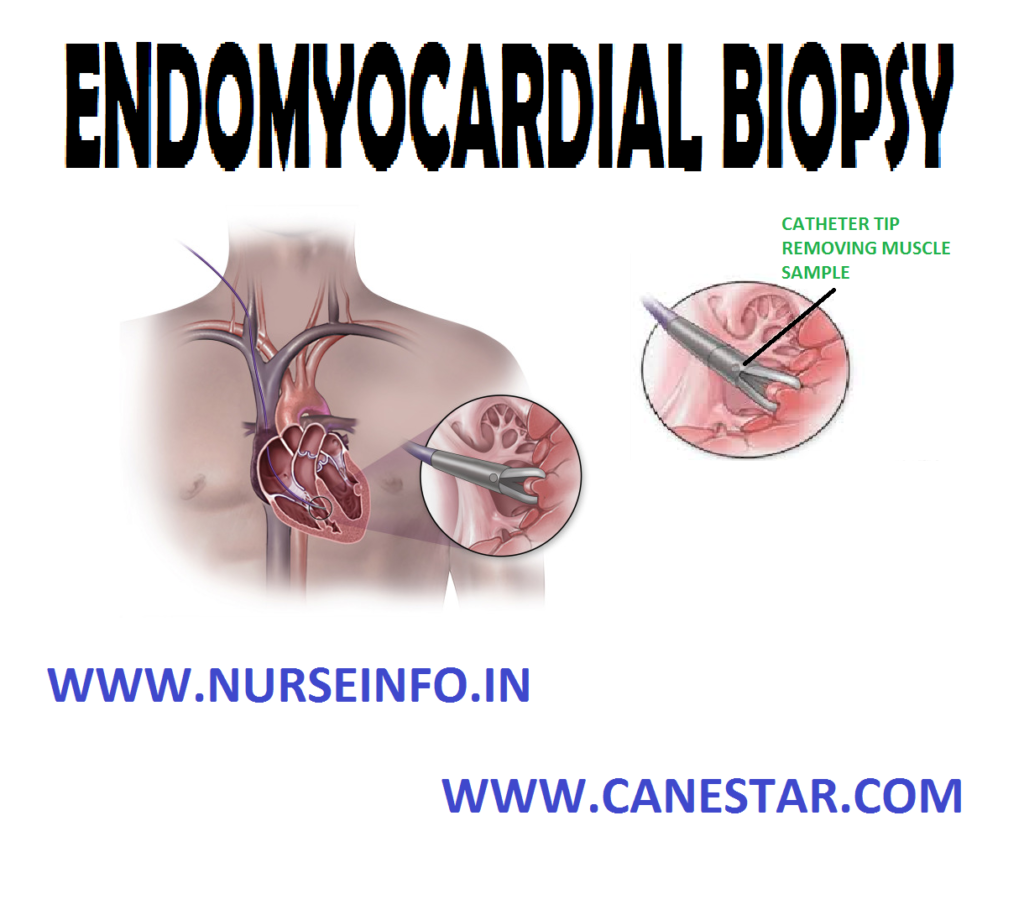
Endomyocardial biopsy is an invasive procedure requiring cardiac catheterization. It permits sampling of right or left ventricular tissue
PURPOSE
- An endomyocardial biopsy is usually performed to determine if a transplanted heart is being rejected
- To diagnose myocarditis or doxorubicin (adriamycin) induced cardiomyopathy
- To determine the cause of restrictive heart disease
FINDINGS
- Doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy
- Cardiac amyloidosis
- Cardiac fibrosis (especially radiation injury)
- Changes cardiomyopathy
- Myocarditis
- Rejection of transplanted heart
- Scleroderma
- Toxoplasmosis
- Tumor infiltrates
- Vasculitis
INTERFERING FACTORS
- Bleeding disorders
- Severe thrombocytopenia
- Systemic anticoagulation
- Uncooperative client
CLIENT PREPARATION
- Instruct the client about the purpose and procedure
- Inform the client that the table rotates and that the physician may ask the client to change positions or cough
- Explain the client that when the dye is given, a feeling of warmth or flushing or a metallic taste may be tensed
- Assist the precatheterization evaluation: blood test, including a prothrombin time test and a partial thromboplastin time test; an electrocardiogram; and chest X-ray
- Obtain client’s height and weight
- Assess the client fear and anxiety. Correct any misconceptions and reassure the client that the nurse, physician and technicians to assist during the procedure will be continuously present
- If contrast dye is going to be used, check all allergies
- Keep the client nothing per oral after midnight, except if the catheterization is planned for late in the afternoon. In that case, a clear liquid breakfast may be given
- Withhold the cardiac drugs as per the physician order
- Prepare catheter site according to laboratory protocols. The femoral artery is commonly used for the percutaneous of the catheter. Usually, both side of the groin are prepared
- Premedication is given as ordered to reduce the client’s anxiety. In some catheterization laboratories, the client is premediated to decrease the risk of allergic reaction to the contrast dye
- Instruct the client to void before going to the catheterization laboratory
PROCEDURE
- The procedure involves a cardiac catheterization
- A catheter with a jaw like tip id inserted under fluoroscopy, and several small tissue samples are obtained
- A right or left ventricular sample may be taken. For clients at high risk, such as those with a history of left ventricular thrombus or infarction, a right ventricular biopsy may be performed
AFTER CARE
- Observe the insertion site of bleeding. Palpate around the punctured site to detect bleeding into tissue
- If bleeding is present, exert pressure just proximal to the puncture site with a gloved hand for a minimum of 15 minutes
- Monitor vital signs and cardiac monitor according to hospital protocol
- Check the distal pulse for artery patency
- Report immediately if any significant changes in vital signs, rhythm and circulation or occurrence of chest pain
- Assess post-procedure laboratory values, such as blood count, prothrombin time, electrolytes and creatine
- Instruct the client about strict bed rest for 12-24 hours and to keep affected extremity straight for 12 hours
- Encourage plenty of oral fluids
- Record type of cardiac catheterization done and client’s tolerance of the procedure
COMPLICATIONS
- Accidental biopsy of papillary muscle or chordate tendineae
- Hemopericardium
- Cardiac perforation