COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHY (BRAIN) – Definition, Purposes, Indications, Preparation of the Client, Procedure, After Care, Complications, Contraindications, Side Effects and Advantages
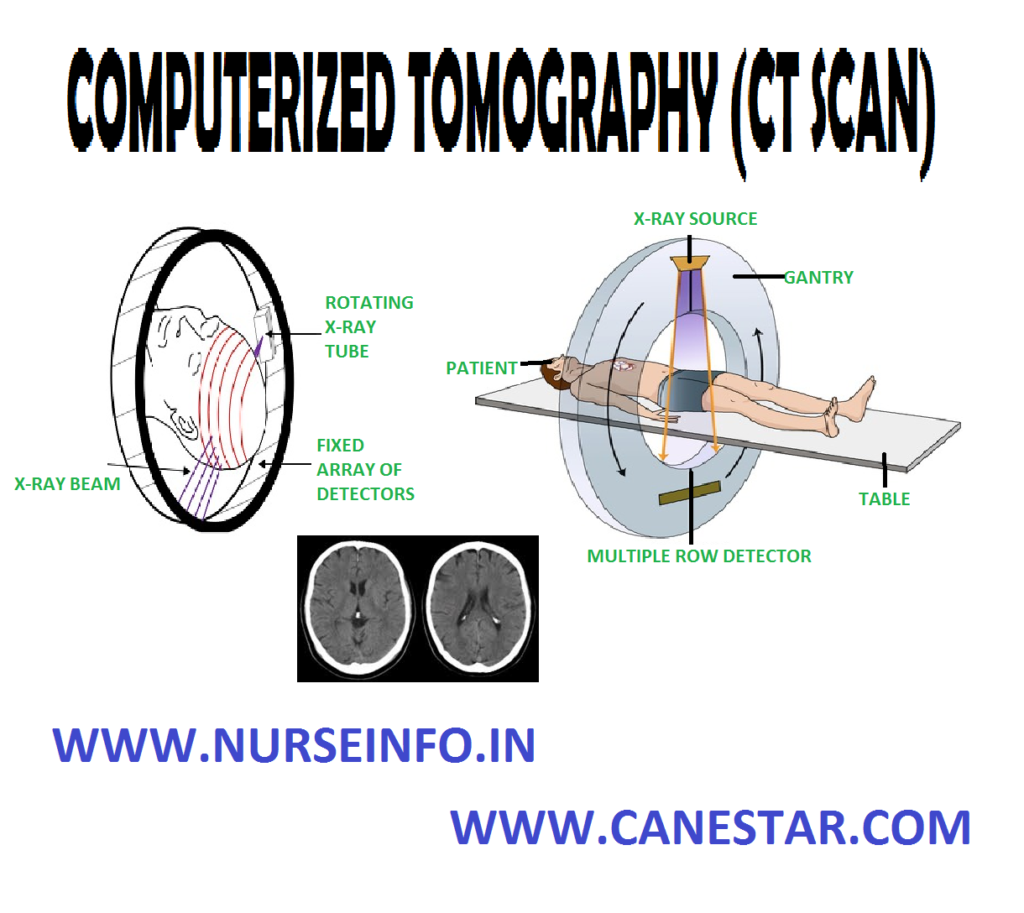
Computerized tomography (CT) scan was developed by Godfry Hounsefield, a British physicist in 1972, for this invention he was awarded Nobel Prize in 1978. In theoretical basis of this technique was provided by Indian biophysicist Gopalsamudian N. Ramachandran. CT scan is 100 times more sensitive than the conventional X-ray so it detects a fine structure and small changes in density
DEFINITION
Computerized tomography is a computerized X-ray procedure used to obtain detailed images of structures within a selected plane of the body. The computer calculates the amount of X-ray penetration of each tissue and displays this image in shades of grey color
PURPOSE
- It provides precise anatomical and pathological information
- Surgical procedures can be done by using CT-guided procedure, e.g. biopsy
- It provides a complete image which helps to decide surgical intervention
- To detect intracranial tumors
INDICATIONS
- Space occupying lesions
- Primary and secondary tumors
- Cerebral edema
- Intracranial hemorrhages
- Arteriovenous malfunction
- Infarctions and aneurysms
PREPARATION OF THE CLIENT
- Explain the procedure to the patient and to the relatives
- Obtain a written consent form the patient or relatives
- Detailed allergic reactions such as iodine
- Jewelry, eye glasses and metal objects shall be removed from the head
- No dietary restrictions if contrast is not given
- If contrast is planned, the client should keep fasting overnight
- For children and restless patients, sedation may be given
- Explain the side effects, which may occur during the procedure
- Arrange emergency medications and articles ready
- For some children or adults who are not cooperating or having involuntary movements, CT-scan may be done under general anesthesia
- Before radioplaque contrast medium is administered, a skin test to be done to check the allergic reactions
- During contrast administration ask the client to take deep breathing till the injection is completed
PROCEDURE
- Place the client comfortably on the table
- Inform the client not to move during the procedure
- Assist the administration of dye
- Place the client’s face uncovered and head immobilized
- The head is scanned numerous times at different angles
- CT scan gives three-dimensional parts
- The entire procedure lasts for 15-30 minutes
AFTER CARE
- Observe the client who received contrast medium for allergic reactions
- Patients who had CT scan under general anesthesia is kept on IV fluids and nothing per month for a few hours
- Encourage more fluid intake to minimize dehydration caused by fasting
- Maintain an intake and output chart promptly
- Check the vital signs
COMPLICATIONS
- Local and systemic allergic reactions
- Spasm or occlusion of the vessels by a clot
- Bleeding at the injection site
- Hematoma formation
- Cardiac arrest
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Hyperthyroidism
- Hypersensitivity to iodine contrast media
SIDE EFFECTS
It mainly caused due to the use of iodinated contrast
- Nausea and vomiting
- Erythematic and sensation of pain
- A general feeling of warmth
- Chills, fever, sweating and headache
- Dizziness, weakness, and suffocation
ADVANTAGES
- It is a painless and safe procedure
- It provides detailed information for diagnosis
- The cost is reasonable
- It can be performed on both conscious and unconscious patients
- Radiation exposure is relatively low compared to that of skull films