INTRAVENOUS INJECTION
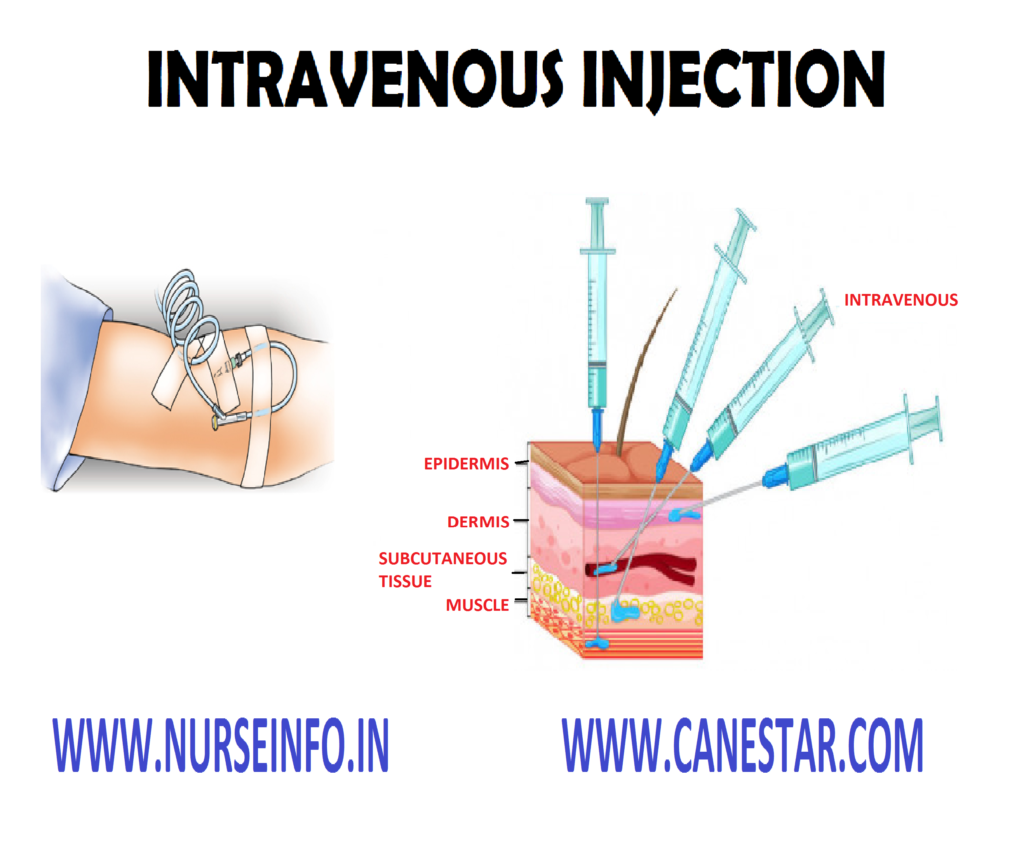
Intravenous injection (IV) is the introduction of a small quantity of drug into the vein by venous puncture
Introduction of drug directly into the bloodstream is called intravenous injection
Purpose
- To have a fast action of the medicine as in emergency
- To give medicines those are irritating or ineffective when given by other routes
- To have the action of medicines on the blood stream or the blood vessels
Common Sites for IV Injection
- Ventral aspect of elbow or forearm median cubical, basilica or cephalic veins
- Doral aspect of hand – branchial, cephalic or metacarpal veins
- In the infants the scalp vein is used
General Instructions
Expel the air from the syringe before giving the injection by holding it in upright position and gently pressing the piston until a drop of solution comes to the tip of the needle
- Always dissolve the drug in correct amount of fluid to minimize the risk of adverse effect of the medicine
- Observe the patient closely for the signs of adverse reaction of the medicine and have emergency drugs and the antidote in hand while injecting the medicine
- Do not give the medicine if the injection site shows any edema or intravenous solution is not following properly to avoid accidental administration of medicine into the surrounding tissues
- When giving iron preparation always confirms that the patient is not sensitive to it by giving a test done
Types of IV Administration
- Adding the medicine in intravenous solution bottle (intravenous infusion)
- Existing intravenous line for continuous infusion
- Bolus: direct intravenous push for immediate or fast action
Selection of Syringe and Needle
- The size of syringe used for intravenous infusion depends upon the amount of fluids to be injected
- Size of the needle used are 18 to 21 gauge or 1 to 2 inches
Preliminary Assessment
Check
- The diagnosis and age of the patient
- The purpose of injection
- The doctors order for the type, dosage, time and route of administration
- The patient’s name and bed number
- The nurses record to find out the time at which the last dose was given
- The symptoms of overdose or allergic reaction
- The necessity for giving test dose
- The form of the medicine available and correct method of administration
- The level of consciousness of the patient
- The site and previous experience of the patient
Equipment
A tray containing
- Syringe and needles of various sizes according to the need in a covered tray (sterile)
- Transfer forceps in a jar containing antiseptic solution
- Sterile cotton swabs and gauze pieces in sterile containers
- Methylated spirit in a container
- Bowl with water
- Tourniquet
- Water for injection
- Drug order sheet
- File to cut open the ampoules
- Small covered tray (sterile)
Preparation of the Patient and Environment
- Identify the patient correctly
- Explain the procedure to the patient
- Provide privacy
- Place the patient in comfortable and relaxed position suitable of intravenous injection
- Select a site suitable for the route of administration, quantity of medication to be given and characteristics of medication
Procedure
- Read the doctors order and select the medication
- Wash hands
- Select appropriate syringe and needle and check whether they are in good working order
- Recheck the order, medicine card with the label of the medicine, expiry date, etc
- Mix well and take out the required amount of solution in the syringe
- Carry medicine to the patient
Method of Administering IV Infection
- Apply a tourniquet on the upper arm
- Ask the patient to clench and unclench the hand
- Pull the skin taut and place the needle in line with vein at a 15 to 45 degree angle
- Insert the needle, a bit below the point where the needle will pierce the vein
- When the back flow of blood occurs into the syringe release the tourniquet and injects the medicine very slowly
- Pressure with swab at the puncture site after the needle is withdrawn to prevent bleeding
After Care
- Observe the area for bleeding if bleeding occurs apply pressure but do not massage
- Give comfortable position to the patient
- Ask the patient to take rest at least 15 to 30 minutes so that you can observe him for any reaction
- Observe the patient for any allergic reaction
- Replace the equipment used for injection
- Clean all other articles and replace them in their proper place
- Wash hands
- Record the procedure on the nurse record sheet and medication sheet
Complications
- Allergic reactions
- Pain
- Injection abscess
- Injury to nerves
- Air embolism